Improving India's Digital Economy with the RBI Security Framework

In 2016, due to the increasing use of information technology by banks and their customers, and the increase in cyber attacks against the financial sector, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) provided cybersecurity guidelines to the country’s banks. Cyber Security Framework in Banks includes an Annex detailing minimum baseline requirements for network security and resilience. These requirements cover such areas as inventory management, secure configuration, patch management, access control, and advanced real-time threat defense. Tenable offers several SecurityCenter® dashboards to help monitor conformance with the RBI guidelines.
Implications of the RBI Framework
The Framework elevates security to a Board/C-level problem
Guidelines have been published by the RBI in the past, but they have not been widely embraced by the various financial service institutions (FSIs). The ramifications of these new guidelines are significant; the Framework elevates security to a Board/C-level problem rather than just something that’s pushed to the technology organization. This means that the priority of security operations will be elevated, that the most senior levels of management will be aware of and involved in risk management and security related decisions, and that this level of management will be monitoring the situation regularly.
The guidelines also mandate the need for continuous real-time monitoring of the security situation, so breaches will be detected and mitigated early rather than later in the attack lifecycle. This is especially important as India moves to a digital economy. Additional emphasis focuses on customer protection, cyber resilience and sharing of information between banks through reporting.
SecurityCenter dashboards
Tenable SecurityCenter Continuous View® (SecurityCenter CV™) offers several specialized dashboards that can help you comply with the requirements specified in the RBI Framework.
Without proper inventory management, unauthorized software and rogue devices could infiltrate your network
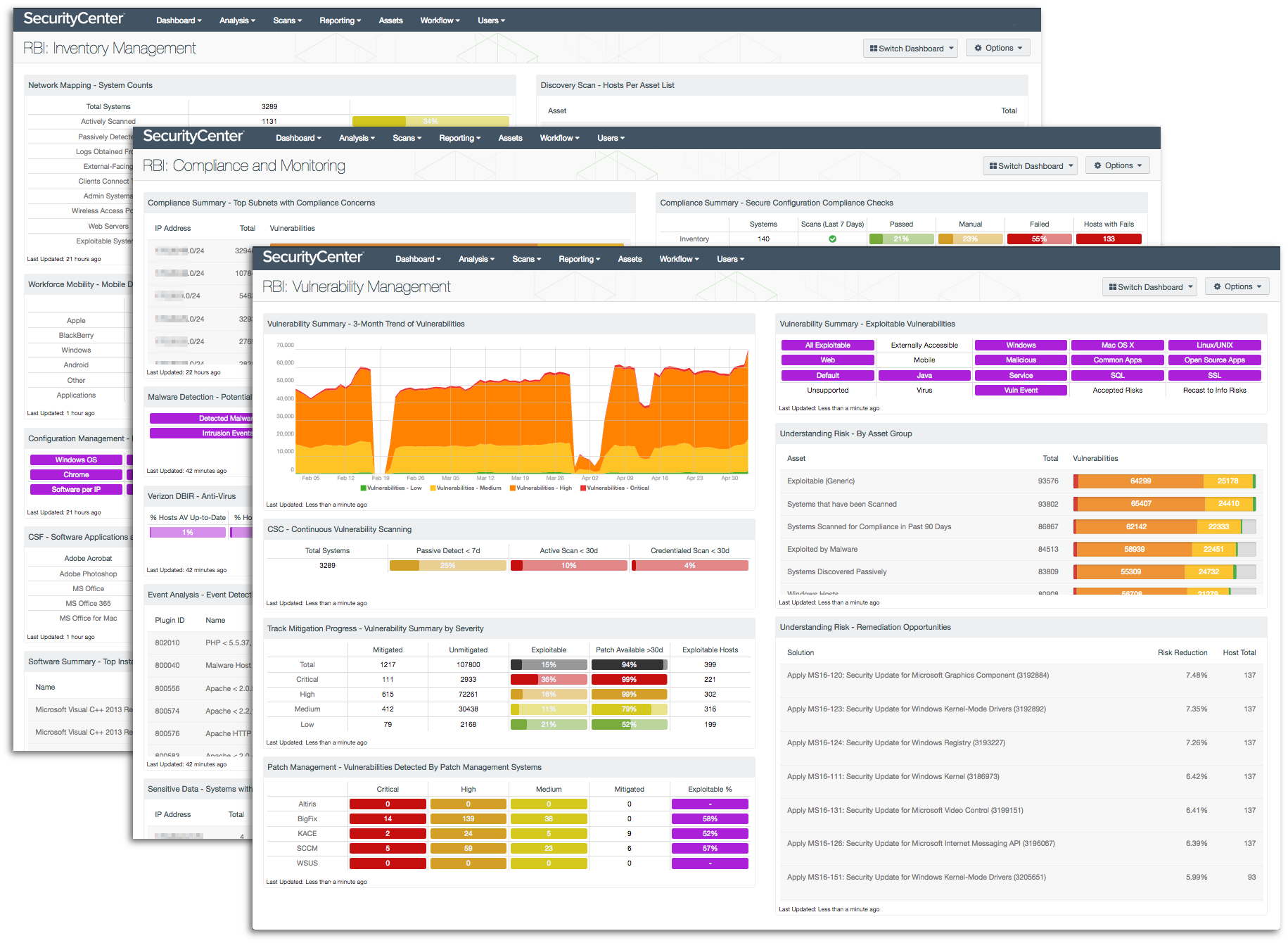
Without proper inventory management, unauthorized software and rogue devices could infiltrate your network, bringing new vulnerabilities and increasing the risk of dangerous network attacks and compromises of sensitive data. The RBI Framework covers good inventory management in baseline controls 1 (Inventory Management) and 2 (Prevent Execution of Unauthorised Software), as well as in other baseline controls that mention identifying mobile devices and controlling software installation. The RBI: Inventory Management dashboard provides an overview of system counts, mobile devices, new MAC addresses, installed software, cloud service use and changes detected throughout your network. This information will enable you to gain control over your inventory and better secure your network.
Network vulnerabilities can lead to critical failures of devices, dangerous network attacks, and compromise of sensitive data
Network vulnerabilities can lead to critical failures of devices, dangerous network attacks, and compromise of sensitive data. The RBI Framework covers vulnerability and patch management in paragraph 6 ("Testing for vulnerabilities at reasonable intervals…") and baseline controls 7 (Patch/Vulnerability and Change Management) and 18 (Vulnerability Assessment). The RBI: Vulnerability Management dashboard provides clear information about detected vulnerabilities and helps you to identify where vulnerability remediation efforts can best pay off. Having accurate information to confidently address vulnerabilities and track remediation progress will enable you to reduce risk to a manageable level in a timely manner.
Without continuously monitoring network activity, unusual activity that could be dangerous or malicious in nature might never be seen
Of course, optimal network security requires more than just preventive measures. Without monitoring configuration compliance, misconfigured devices could facilitate actions that put critical systems and sensitive data at risk. Without continuously monitoring network activity, unusual activity that could be dangerous or malicious in nature might never be seen. The RBI Framework covers continuous network monitoring in paragraph 12 ("Banks need to take effective measures … to promptly detect any cyber-intrusions…") and several baseline controls, including 5 (Secure Configuration) and 13 (Advanced Real-time Threat Defence and Management). The RBI: Compliance and Monitoring dashboard helps you lock down and monitor configurations, and detect potentially malicious activity. Continuous monitoring catches cyber attacks early, before serious damage to systems and data can be done.
Other dashboards are available in the Tenable SecurityCenter feed that can assist you in securing your network and thwarting cyber attacks. Some dashboards focus on specific threats or products; find these in the feed by searching for keywords such as “Cisco”, “database”, or “Shellshock”. These dashboards focus attention on specific systems and may be called for in response to specific threats. Other dashboards, like the RBI dashboards discussed above, cover general cyber security concepts and support drilling down into the data to obtain more detailed information. For example:
The RBI Framework is a powerful tool to help banks conform with cybersecurity best practices. Tenable SecurityCenter dashboards help monitor and measure progress against the RBI controls.
Many thanks to David Schwalenberg for his contributions to this article.
- APAC
- Financial Services
- Security Frameworks
- Center for Internet Security (CIS)