Microsoft’s October 2023 Patch Tuesday Addresses 103 CVEs (CVE-2023-36563, CVE-2023-41763)

Microsoft addresses 103 CVEs including two vulnerabilities that were exploited in the wild.
Update October 13: The blog has been updated to include plugin coverage to identify systems with unsupported verions of Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2.
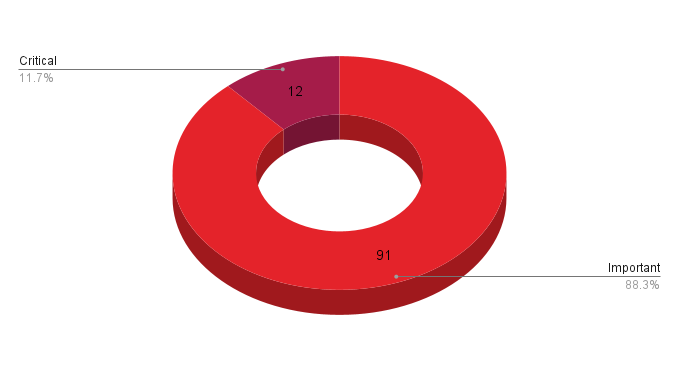
- 12Critical
- 91Important
- 0Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft patched 103 CVEs in its October Patch Tuesday release, with 12 rated as critical and 91 rated as important. We omitted CVE-2023-44487 from our counts as this vulnerability was reported to MITRE and not Microsoft and does not exclusively affect Microsoft products. Details about this flaw are included in our analysis below.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- Active Directory Domain Services
- Azure
- Azure DevOps
- Azure Real Time Operating System
- Azure SDK
- Client Server Run-time Subsystem (CSRSS)
- Microsoft Common Data Model SDK
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft QUIC
- Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
- Microsoft Windows Media Foundation
- Microsoft Windows Search Component
- Microsoft WordPad
- SQL Server
- Skype for Business
- Windows Active Template Library
- Windows AllJoyn API
- Windows Client/Server Runtime Subsystem
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Container Manager Service
- Windows DHCP Server
- Windows Deployment Services
- Windows Error Reporting
- Windows HTML Platform
- Windows IIS
- Windows IKE Extension
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
- Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
- Windows Message Queuing
- Windows Microsoft DirectMusic
- Windows Mixed Reality Developer Tools
- Windows NT OS Kernel
- Windows Named Pipe File System
- Windows Power Management Service
- Windows RDP
- Windows Remote Procedure Call
- Windows Resilient File System (ReFS)
- Windows Runtime C++ Template Library
- Windows Setup Files Cleanup
- Windows TCP/IP
- Windows TPM
- Windows Virtual Trusted Platform Module
- Windows Win32K
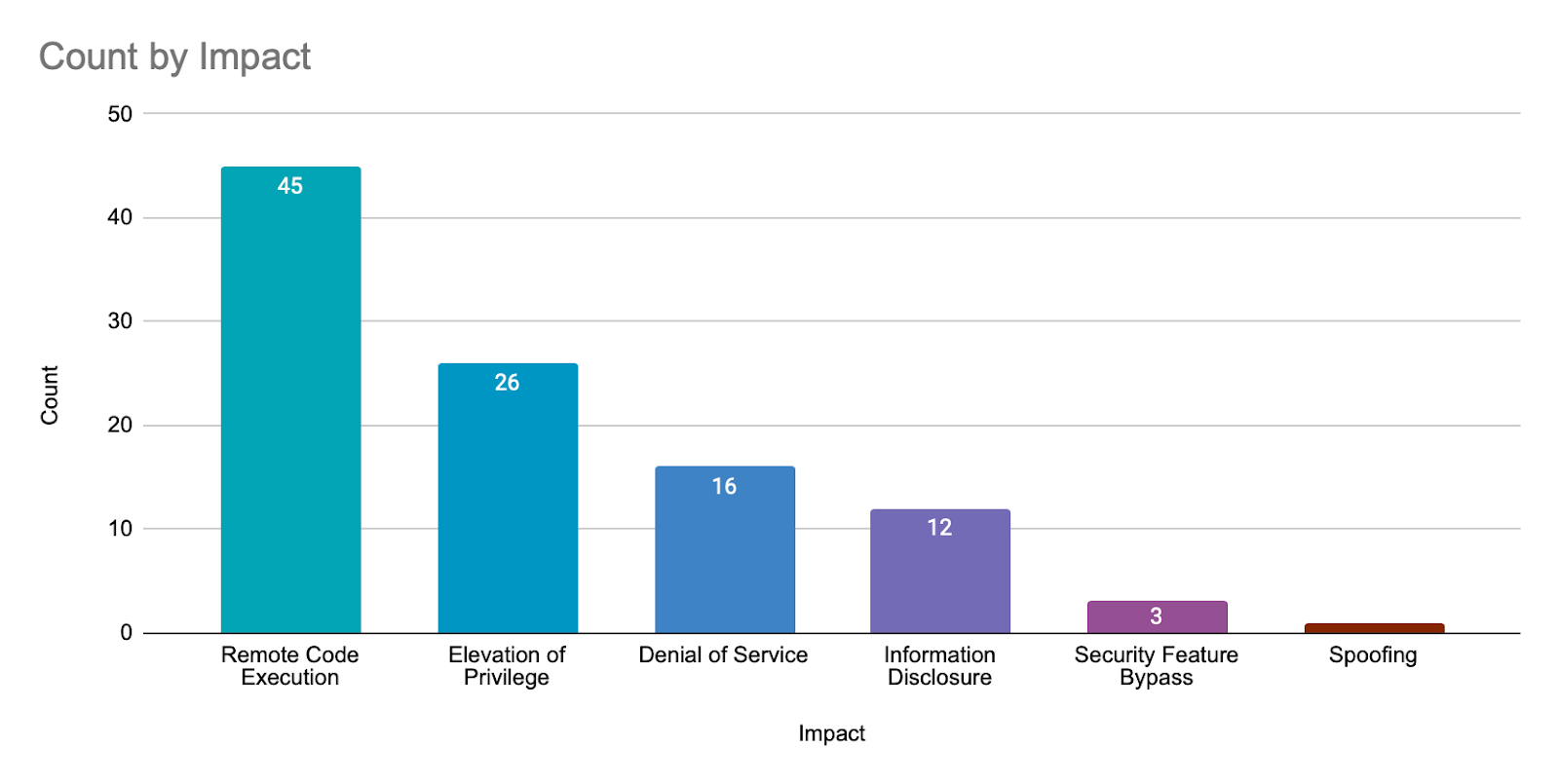
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 43.7% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 25.2%.
CVE-2023-36563 | Microsoft WordPad Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36563 is an information disclosure vulnerability in Microsoft WordPad that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 6.5. It was exploited in the wild as a zero-day and was publicly disclosed prior to the October 2023 Patch Tuesday release. An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability using social engineering in order to convince a target to open a link or download a malicious file and run it on the vulnerable system. Alternatively, an attacker could execute a specially crafted application to exploit the flaw after gaining access to a vulnerable system. Successful exploitation could lead to the disclosure of New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) hashes.
This is the third zero-day vulnerability patched in 2023 that could result in the unauthorized disclosure of NTLM hashes. In March, Microsoft patched CVE-2023-23397, a Microsoft Outlook elevation of privilege vulnerability, and in September, Microsoft patched CVE-2023-36761, an information disclosure vulnerability in Microsoft Word. It is unclear if all three of these vulnerabilities were exploited by the same attackers.
CVE-2023-41763 | Skype for Business Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-41763 is an EoP vulnerability in Skype for Business that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 5.3 and rated important. An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a specially crafted network call to a vulnerable Skype for Business server. Successful exploitation would result in the disclosure of sensitive information, which could be used to gain access to internal networks.
This vulnerability was exploited in the wild according to Microsoft, though no details have been shared at the time this blog post was published. However, this vulnerability is noted to have been publicly disclosed previously. Researcher Florian Hauser of Code White GmbH published a two-part blog series in September 2022 investigating Skype for Business 2019. In his second blog post, Hauser revealed a server-side request forgery vulnerability (SSRF) that he called SKYPErimeterleak. In it, he notes that Microsoft rejected his submission for the flaw. However, it would appear that Microsoft has since opted to accept his submission, assigning this CVE and providing patches for this vulnerability.
CVE-2023-35349 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-35349 is a RCE vulnerability in the Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ) component of Windows operating systems that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8 and rated critical. An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit this vulnerability by sending a specially crafted packet to a vulnerable target.
In addition to CVE-2023-35349, Microsoft has patched 15 additional RCE vulnerabilities in MSMQ:
| CVE | Title | CVSSv3 Score | Exploitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2023-36593 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.8 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36570 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36571 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36582 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36573 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36572 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36591 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36590 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36589 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36592 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36583 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36578 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36574 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36575 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.3 | Exploitation Less Likely |
| CVE-2023-36697 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 6.8 | Exploitation Less Likely |
While CVE-2023-36697 was also rated critical, successful exploitation requires either user interaction or for the attacker to be authenticated as a domain user and to have compromised a MSMQ server within the target network.
CVE-2023-35349 and CVE-2023-36697 are two of several critical RCE vulnerabilities in MSMQ that have been patched this year. CVE-2023-35385, CVE-2023-36910 and CVE-2023-36911 were patched in August, CVE-2023-32057 in July and CVE-2023-21554 in April. Although all of these vulnerabilities were rated “Exploitation Less Likely” using the Microsoft Exploitability Index, customers are encouraged to apply these patches as soon as possible.
In order for a system to be vulnerable to these vulnerabilities, the MSMQ service must be added and enabled. According to Microsoft, if the service is enabled on a Windows installation, a service named “Message Queueing” will be running on TCP port 1801. Tenable customers can use Plugin 174933 to identify systems that have this service running.
CVE-2023-36434 | Windows IIS Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36434 is an EoP vulnerability in Windows IIS server that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8 and rated as important. According to Microsoft, exploitation of this vulnerability is achieved by an attacker brute forcing a user’s login credentials. Because the chances of success can vary greatly and are less likely when strong passwords are in place, Microsoft’s severity rating is important, despite the critical CVSS score.
Weak passwords and password policies can open the door for malicious actors and remain a major risk for organizations. To combat this, we recommend reviewing the suggestions from this Cybersecurty and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) blog post and the Tenable whitepaper, Password, Authentication and Web Best Practices.
CVE-2023-36569 | Microsoft Office Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36569 is an EoP vulnerability in Microsoft Office assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.4 and is rated as important. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability would provide an attacker with SYSTEM level privileges. Microsoft notes that this vulnerability is less likely to be exploited and that the preview pane is not an attack vector for exploiting this vulnerability.
CVE-2023-36778 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36778 is a RCE vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8 and is rated as important. A local, authenticated attacker could exploit this vulnerability through a remote PowerShell session with the target server. The vulnerability is caused by improper validation of cmdlet arguments within Microsoft Exchange Server. CVE-2023-36778 was rated “Exploitation More Likely” using the Microsoft Exploitability Index.
CVE-2023-44487 | HTTP/2 Rapid Reset Attack
CVE-2023-44487 is a denial of service (DoS) vulnerability affecting HTTP/2 web servers that was exploited in the wild. While this vulnerability was not exclusive to affecting Microsoft servers, patches were made available to address this vulnerability in multiple versions of Windows, including Server Core installations.
This vulnerability was exploited against multiple targets in a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack and was first observed by Cloudflare on August 25 and Edgio on August 28th. Cloudflare worked with both Google and Amazon AWS who have acknowledged that additional mitigations are in place to address this vulnerability. As noted in Cloudflare’s technical blog post, the underlying vulnerability is in HTTP/2 and other vendors utilizing HTTP/2 may be affected by the vulnerability. We anticipate additional patches or mitigation guidance will be released by vendors that implement HTTP/2.
Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 End of Life
Microsoft announced that Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 has reached its end of life as of October 10, 2023. This means that users of these versions of Windows Server will no longer receive security updates and should upgrade to a supported version as soon as possible.
To identify hosts with Windows Server 2012 or 2012 R2, the following plugins are available:
| Plugin ID | Description |
|---|---|
| 182965 | Microsoft Windows Server 2012 / 2012 R2 ESU Status Check |
| 182964 | Microsoft Windows Sever 2012 Unsupported Version Detection |
| 182966 | Microsoft Windows Sever 2012 R2 Unsupported Version Detection |
Tenable Solutions
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s October 2023 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
A list of Tenable plugins to identify CVE-2023-44487 can be found in the plugins section of the individual CVE page as they’re released. This link will display all available plugins for this vulnerability, including upcoming plugins in our Plugins Pipeline.
For more specific guidance on best practices for vulnerability assessments, please refer to our blog post on How to Perform Efficient Vulnerability Assessments with Tenable.
Get more information
- Microsoft's October 2023 Security Updates
- Tenable plugins for Microsoft October 2023 Patch Tuesday Security Updates
Change Log
Update October 13: The blog has been updated to include plugin coverage to identify systems with unsupported verions of Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2.
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management


