Verizon’s 2022 Data Breach Report – Insights for Cloud Security Professionals

Wondering which cyberattack trends are putting your organization at risk? Learn about the leading threat vectors — and how cloud security solutions can help.
Since 2008, Verizon, a leading U.S. telecommunications services provider, has been publishing a comprehensive annual report, the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR). The report analyzes the security incidents and data breaches of the previous year, and details cyberattack trends.
The 2022 Verizon report is based on data from more than 80 organizations. Verizon analyzed 23,896 real-world security incidents, of which 5,212 were confirmed breaches. Wondering what the difference is between an "incident" and a "breach"? As described by Verizon: an incident is “a security event that compromises the integrity, confidentiality or availability of an information asset”; a breach is “an incident that results in the confirmed disclosure — not just potential exposure — of data to an unauthorized party.”
The report details its findings by attack type, industry, vulnerability, geography and other parameters. You’ll learn much from reading the full report; here, we provide a summarized version based on findings we think to be of greatest interest to cloud security professionals. Understanding the findings and insights can help you in prioritizing your security efforts.
Let's dive straight in!
Key findings for cloud security professionals
Credentials - The #1 organizational security weakness
Coming in first isn’t always a good thing. This year, Verizon found the “lucky” winner of the leading organizational security weakness to be credentials. Their profound weakness makes credentials the bane of security professionals’ existence.
Per Verizon, “There are four key paths leading to your estate: Credentials, Phishing, Exploiting vulnerabilities and Botnets. These four pervade all areas of the DBIR, and no organization is safe without a plan to handle them all.”
Out of 4,250 data breaches Verizon analyzed, approximately:
- 50% were enabled through credentials
- 15+% were enabled through phishing
- 5+% were enabled through vulnerability exploitation
- The remaining were enabled through botnets

Select enumerations in non-Error, non-Misuse breaches (n=4,250), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
Ransomware rates continue to climb
With every year, ransomware is becoming a more prominent threat. Per Verizon, “This year Ransomware has continued its upward trend with an almost 13% increase — a rise as big as the last five years combined (for a total of 25% this year).” Verizon further found that nearly 70% of malware breaches this year involved ransomware.

Ransomware over time in breaches, Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
How to avoid ransomware? Verizon states that “it’s important to remember, Ransomware by itself is really just a model of monetizing an organization’s access. Blocking the four key paths mentioned above helps to block the most common routes Ransomware uses to invade your network.”
This statement is reinforced through research conducted by Tenable Cloud Security that found “high potential for ransomware in organizations’ environments.” According to the research findings, the ransomware potential was due to misconfigured identities, publicly exposed machines, risky third-party identities and risky access keys.
Misconfigurations: A dominant trend
According to the report, 13% of data breaches were caused by errors. Verizon found this finding to be “heavily influenced by misconfigured cloud storage.” (We explore this metric further in the “miscellaneous errors” section).
The human element and its inherent vulnerability
As humans, we enjoy experiencing emotions and making meaningful connections; our humanness also makes us vulnerable to malicious cyber security actions that lead to breaches. Verizon found that 82% of breaches involved the human element and spanned use of stolen credentials, phishing, misuse and errors. Verizon noted that “people continue to play a very large role in incidents and breaches alike.”
Web application hacking: The main driving force behind incidents and attacks
Per Verizon, hacking incidents are “attempts to intentionally access or harm information assets without (or exceeding) authorization by circumventing or thwarting logical security mechanisms.”
This year, attackers exploited web applications more than any other attack vector to gain access to organizational systems. Specifically, web application hacking was the number one action vector for both incidents and attacks, causing ~70% of incidents and ~45% of actual attacks.

Top Action vectors in incidents (n=18,419), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report

Top Action vectors in breaches (n=3,279), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
Says Verizon, “these align well with the notion that the main ways in which your business is exposed to the internet are the main ways that your business is exposed to the bad guys… Unfortunately, if you can access the asset directly over the internet simply by entering the credentials, so can the criminals.”
As has been stressed before, this datapoint makes it all the more important to gain visibility into misconfigurations and permissions management. Indeed, Verizon found that more than 40% of attacks occurred due to hacking using stolen credentials and more than 20% due to ransomware (which can be the outcome of misconfigurations).

Top Action varieties in breaches (n=3,875), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
Credentials: A vicious cycle
During attacks, hackers compromise data. But which data is usually targeted? According to Verizon, “the top two data types are now Credentials and Personal data. We’ve long held that Credentials are the favorite data type of criminal actors because they are so useful for masquerading as legitimate users on the system. Much like the proverbial wolf in sheep’s clothing, their actions appear innocuous until they attack.”
In other words, credentials are often used to breach systems and are also compromised during breaches. They are then used for lateral movement that further compromises data, like personal data compromising, which Verizon notes as useful for financial fraud.

Top Confidentiality data varieties over time in breaches, Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
What do attackers do in systems? Verizon notes that, “Once attackers are inside the victim's network they often install malware which violates the Integrity of a system (as does any other illicit change).” Verizon found that more than 30% of breaches included malware.
Verizon also noted that a person’s integrity, “can also be compromised when they alter their behavior due to the actions of the adversary. Examples include responding to a phishing email or falling victim to a pretexting scenario.” See more in the “social engineering” section below.
Incident classification patterns and who they affected
The DBIR report analyzed and classified a total of 23,896 incidents by type of vulnerability or attack. We cite below the main incident types that can impact an organization’s public cloud and have also added a short recommendation on how a cloud security solution might help prevent them.
System intrusion by third parties
Verizon defines third-party breaches as a single breach in which a third party is compromised; the breached victim is not the owner of the data. Verizon found a low incidence of third party breaches — only 1% of the study’s breach data. Yet when broken down, the data revealed that more than 50% of third party breaches were attributable to stolen credentials and approximately 40% of them to ransomware.

Top Action varieties in third-party incidents (n=73), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
In many cybersecurity articles and reports, supply chain breaches are often grouped together with third parties, but Verizon analyzes them separately. And rightfully so: Verizon found that the supply chain was responsible for 62% of system intrusion incidents this year.
Per Verizon, supply chain breaches are defined as “a sequence of one or more breaches chained together… this may be a breach where there are secondary victims (when seen from the primary victim’s breach) or where a partner was the vector (when seen from the secondary victim’s breach).” Verizon cited another common example as when a software vendor is exploited to push a malicious update to organizations or when a compromised partner and set of credentials are used to gain access. Backdoor incidents are the cause of most of these attacks.

Top varieties in Supply Chain incidents (n=2,103), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
How a cloud security solution can help prevent system intrusion
A cloud security solution helps reduce weaknesses caused by external actors like partners, vendors and supply chains (as well as internal employees and cloud services). The thousands of identities associated with these entities pose potential identity and access risks. A cloud security solution enforces least privilege that limits the inappropriate credentials use, detects anomalous behavior and helps reduce exposure to malware and ransomware.
Scratching the surface
How do attackers find software and system security weaknesses? According to Verizon, “they start with scanning for IPs and open ports. Then they move to crawling for specific services. They then move on to testing for specific Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE). Finally, they try Remote Code Execution (RCE) to gain access to the system.” This means that the better the organization’s cloud security posture, the less of a chance that attackers will be able to find and exploit vulnerabilities.
In terms of security, Verizon found that organizations fall into one of four organizational categories:
- Secure (or at least actively trying to be secure),
- Ransomware (organization with a disclosed ransomware incident),
- Random (organizations chosen purely at random)
- Breached (organizations that had suffered a breach)
What’s the difference between each category? Says Verizon, “while security-concerned organizations run a pretty tight ship, the other three have organizations out in the tail with far more vulnerabilities per internet-facing host. And if you wonder who the threat actors… are looking for, it’s the organizations in that tail. Remember that for many attackers it’s simply a numbers game — they just want some amount of access — and those tails still provide enough of an incentive for them to continue to try the exploits until they get lucky.” So getting attacked is often not about karma or force majeure, just about how prepared you were with security controls and processes in place.
Here’s more about what drives attackers and what they’re looking for.
How a cloud security solution can help
Strategically, the security readiness of an organization depends on a number of factors. These include the technologies they’ve chosen, the processes they have in place and the human talent holding security positions. A comprehensive cloud security platform that provides a wide range of capabilities across multiple security categories can help organizations achieve readiness and incrementally improve their cloud security maturity and ability to thwart threats and ensure compliance. At Tenable Cloud Security, we’ve developed a cloud security maturity model that can help organizations map where they are and how to get to the next step.
In addition, a cloud security solution can preempt attackers’ scanning, crawling and testing activities and identify any misconfigurations in advance. These misconfigurations can then be automatically remediated, reducing the chances of the organization to leave a “tail” for attackers to exploit.
Social engineering
Social engineering, according to Verizon, is the “psychological compromise of a person that alters their behavior into taking an action or breaching confidentiality” — for example, phishing, bribery, extortion and more. Verizon analyzed 2,249 social engineering incidents, 1,063 of them with confirmed data disclosure.
Credentials represented nearly two thirds (63%) of compromised data. While approximately 70% of social engineering attacks were caused because of phishing, approximately 30% leveraged stolen credentials, which brings us back to the vicious cycle of using credentials to obtain credentials and thus progressing laterally in organizational systems.

Action varieties in Social Engineering breaches (n=1,063), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
What do attackers do once they’ve successfully socially engineered their way into systems? According to the Verizon report, “In breaches, providing a Backdoor or Command and Control (C2), followed by delivering a Downloader are the top two things actors are looking to do once their successful phish lands their malware. If the phish busts through the door… the Backdoor, C2 and Downloader hold it open for all the rest of the actions to make their way in.”
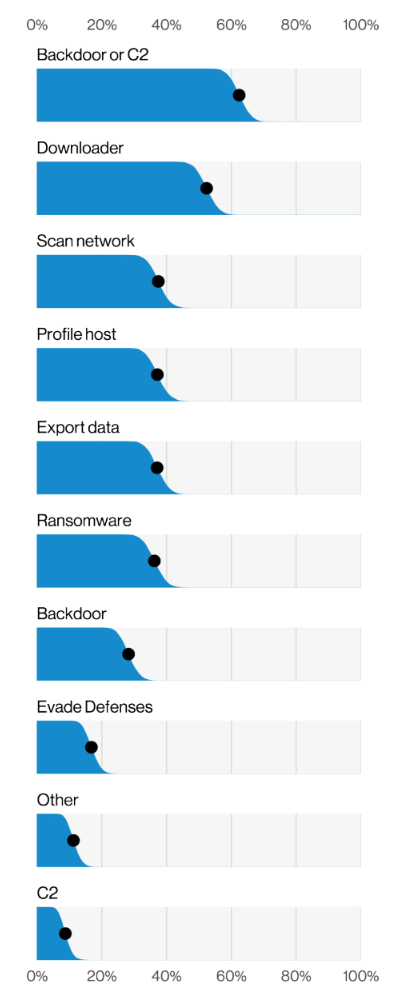
Top Malware varieties in Social Engineering breaches (n=235), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
How a cloud security solution can help prevent social engineering
Social engineering is the manipulation of human behavior. And while no technological platform can make us unhuman (yet…), technology can help minimize the blast radius of human error.
If an employee or third party is the victim of social engineering, a cloud security solution can minimize the use of stolen credentials, help identify anomalous behavior and minimize malware injections by preventing misconfigurations. These capabilities can help prevent real-time abuse and can also be used for investigation in retrospect.
We also subscribe to Verizon’s notion that “training is a big part of improving.” Leveraging a user-friendly cloud security solution can help train engineers about risks and least privilege to help minimize vulnerability prevalence in the infrastructure.
Basic web application attacks
The Verizon report states that basic web application attacks are “attacks against a Web application, and after initial compromise, they do not have a large number of additional Actions. It is the ‘get in, get the data and get out’ pattern. … These incidents leverage one or the other of two entry points, the Use of stolen credentials or Exploiting a vulnerability.”
Why do these types of attacks occur? Verizon identified a clear trend: “This pattern continues to largely be dominated by the Use of stolen credentials to access an organization’s internet-facing infrastructure, like web servers and email servers.” Verizon has also identified another interesting pattern: “an almost 30% increase in stolen credentials since 2017, cementing it as one of the most tried-and-true methods to gain access to an organization for the past four years.”
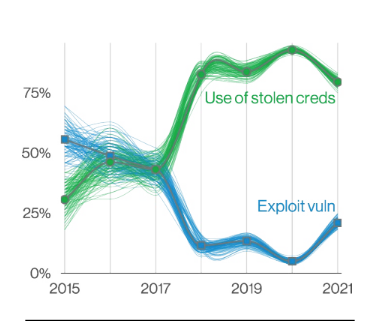
Exploit vulnerable vs Stolen credentials over time in Basic Web Application Attacks breaches, Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
In fact, as early as 2009, Verizon called out identity mismanagement as a leading cause of these attacks. In 2009 they stated that “it is evident that many intrusions exploit the basic (mis)management of identity. Unauthorized access via default, shared, or stolen credentials constituted more than a third of the entire Hacking category and over half of all compromised records. It is particularly disconcerting that so many large breaches stem from the use of default and/or shared credentials, given the relative ease with which these attacks could be prevented.”
Out of 4,751 incidents and 1,273 with confirmed data disclosure analyzed, Verizon found that stolen credentials were used in more than 80% of these attacks.

Top Action varieties in Basic Web Application Attacks breaches (n=962), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
According to Verizon, once inside, attackers mostly go after web applications, but also “Mail servers, which represented less than 20% of the total breaches in this pattern. Of those Mail servers, 80% were compromised with stolen credentials and 30% were compromised using some form of exploit. While this 30% may not seem like an extremely high number, the targeting of mail servers using exploits has increased dramatically since last year, when it accounted for only 3% of the breaches.”

Top Asset varieties in Basic Web Application Attacks breaches (n=1,001), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
How a cloud security solution can help prevent basic web application attacks
Web application attacks occur mainly due to stolen credentials. An average company has thousands of human and machine identities that determine access to compute resources or data — making them very difficult to track and govern.
A cloud security solution can reduce the complexity of managing access and configuration risks by providing visibility into all identities, human and service, and their permissions — and contextual analysis of access risk. This helps identify toxic combinations, enforce the principle of least privilege including through just-in-time (JIT) developer access, detect anomalous user behavior and pinpoint misconfigurations. Such continuous risk assessment (and automated remediation, also enabled through a cloud security solution) can help prevent hackers from obtaining stolen credentials and/or exploiting them to progress laterally.
Miscellaneous (human) errors
According to Verizon, miscellaneous errors are “incidents where unintentional actions directly compromised a security attribute of an information asset.”
Interestingly, Verizon found that this year, the main persona in such errors was not partners, but rather “about your employees.” When it comes to human misconfiguration errors, says Verizon, “misconfiguration is frequently paired with the Discovery Method of “Security Researcher.”
Out of 715 incidents analyzed, a hefty number of 708 resulted in confirmed data disclosure.
How do misconfigurations occur? Verizon comments that “the rise of the Misconfiguration error began in 2018 and was largely driven by cloud data store implementations that were stood up without appropriate access controls.” Verizon emphasizes the difficulty of relying on cloud providers: “Despite the efforts of the major cloud providers to make the default configurations more secure (which we applaud), these errors persist.”
What are the consequences of these human errors? Quite severe, apparently. Notes Verizon: “The data types involved in these breaches are still overwhelmingly of the Personal variety. Medical and Banking information are occasionally involved, but they are not the norm. The data tends to be from customers, and it is also the customers who are notifying the breached organizations in a high number of cases. However, Security researchers are still the stars of this Discovery show (although their percentage is down from last year).”
While the DBIR does not comment on why this change occurred, we contemplate this might be due to increased awareness by customers, overwhelmed security personnel or security shifting left and many errors that were previously identified by researchers are now being caught earlier.
How a cloud security solution can help prevent miscellaneous errors
Misconfigurations can (and often do) lead to cloud infrastructure security weaknesses. A cloud security solution can help prevent these weaknesses by identifying these misconfigurations, prioritizing the risks and then mitigating the weaknesses — before they are discovered by attackers and thus reducing the attack surface. A cloud security solution also fills in the security gaps left by public cloud providers as part of the shared responsibility model, while reducing the cloud attack surface.
Privilege misuse
Privilege misuse, according to Verizon, refers to the “incidents predominantly driven by unapproved or malicious use of legitimate privileges.” This category is mostly about internal employees stealing data maliciously by exploiting their access.
Out of 275 incidents, 216 of them with confirmed data disclosure, Verizon discovered that more than 80% of incidents occurred due to privilege abuse:

Top Action varieties in Privilege Misuse breaches (n=176), Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
Yet, data mishandling is also not to be overlooked. Per Verizon, data mishandling “is typically associated with the motive of Convenience. Sometimes people do unsafe things to get around a security control designed to protect the data from exposure.”
We subscribe to Verizon’s notion that “while some controls may make it harder for people to get their jobs done, it is important to pair these controls with education to at least let people know the ‘why’ behind the process. Regardless, offering a less laborious process that remains secure would be something to consider if your organization repeatedly suffers this kind of event.”
How a cloud security solution can help prevent privilege misuse
By continuously identifying and removing risky access, a centralized, identity-focused cloud security solution can help prevent privilege misuse — both accidental and malicious (abuse) — and raise organizational security levels. Addressing organizational processes and educating people — with help of such a platform and its visibility — will also make a major impact on securing cloud identities. Using the platform will enforce least privilege that in turn limits malicious abuse of privileges. Also, by detecting anomalous behavior, it will help identify irregular activities that might point to abuse of permissions that is in progress. Continuous risk assessment and contextual visibility are key to preventing such actions.
What about innocent data mishandling? The same rules apply. By limiting permissions and detecting irregular behavior, these actions — and the potentially consequential data breaches — can be prevented.
Industries — What to look out for
In addition to its cross-industry outlook on incidents and breaches, Verizon also provides insights into the unique attacks each industry is subject to. Here are a number of the industries the Verizon report covers:
Financial and insurance
In the financial and insurance industry, Verizon found 2,527 incidents, 690 with confirmed data disclosure. Of them, 79% were caused by basic web application attacks, system intrusion or miscellaneous errors. It’s interesting to note that, as per Verizon, in the finance and insurance industry, “System Intrusion has doubled from 14% in 2016 to 30% this year.”
To deal with these threats, the top recommended Center for Internet Security (CIS) guidance is to enforce these following Implementation Group 1 (IG1) protective controls:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Secure configuration of enterprise assets and software
- Data protection
Healthcare
In healthcare, Verizon identified and analyzed 849 incidents, 571 with confirmed data disclosure. Of them, 76% were caused by basic web application attacks, system intrusion or miscellaneous errors.
What’s the cause of all these errors? Per Verizon, “Employees are still causing breaches, but they are more than 2.5 times more likely to make an error than to maliciously misuse their access. Misdelivery and Loss are the most common errors (and they are so close, we’d need a photo finish to determine a winner).”
To deal with these threats, the top recommended CIS guidance is to enforce these following Implementation Group 1 (IG1) protective controls:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Secure configuration of enterprise assets and software
- Access control management
Information
In 2022, Verizon researched 2,561 incidents, 378 of them with confirmed data disclosure. Of them, 81% were caused due to basic web application attacks, system intrusion or miscellaneous errors.
System intrusion is the top breach pattern in the information industry. According to Verizon, “One interesting effect of having System Intrusion in the number one position is that the Information industry contains a smorgasbord of Action varieties. Use of stolen creds is the most common, but after that, a legion of varieties are present, with Ransomware, Misconfiguration, Backdoor or C2, and Export Data appearing in more than 4% of breaches.”
CIS IG1 recommendations:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Secure configuration of enterprise assets and software
- Access control management
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, Verizon analyzed 2,337 incidents, 338 of them with confirmed data disclosure. Of them, 88% occurred due to system intrusion, basic web application attacks or social engineering – and external actors.
The CIS IG1 protective recommendations are:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Access control management
- Secure configuration of enterprise assets and software
Mining, quarrying, oil & gas, utilities
Out of 403 incidents Verizon analyzed, 179 had confirmed data disclosure. A hefty 95% of them occurred due to social engineering, system intrusion or basic web application attacks. A very large percentage of the data compromised, 73%, was credentials.
The recommended CIS IG1 protective controls are:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Access control management
- Account management
Public administration
Verizon analyzed 2,792 incidents, 537 of them with confirmed data disclosure. Last year, social engineering was a significant cause of public administration attacks (69%). This year, system intrusion, miscellaneous errors and basic Web application attacks represented 81% of breaches. Per Verizon, “In part, this may be attributed to some prominent and far-reaching supply chain breaches that came to light last year.”
The top recommended CIS IG1 protective controls are:
- Security awareness and skills training
- Access control management
- Account management
Conclusion
Combating cyberattacks is challenging because security professionals are often fighting them in the dark. Teams have limited visibility into where the next attack will come from, and how extensive it will be. That’s why reports like Verizon DBIR are helpful -- they shed light on types of attacks and the vulnerabilities exploited, helping security professionals better prepare for and reduce the risk of being attacked themselves.
A comprehensive cloud security solution — and a cloud security maturity strategy — can help you address the risks like those presented in the report. Offering contextual visibility across the full cloud stack of data, compute, network and identity, and assessing, prioritizing and automatically remediating access risks, so solutions can help eliminate many of the security weaknesses presented in the report before they reach production. They can also facilitate your organization's implementation of zero trust and least privilege principles, including through JIT access, significantly reducing your cloud environment's blast radius.
Finding the right cloud security solution is step one. Step two is implementing a plan for achieving cloud security maturity and coordinating processes, solutions and people together to shift left on security and minimize your cloud attack surface. Security is a collaborative, cross-organizational effort. Together with the right tools, you can protect your organization’s cloud environment.
* All quotations and images are sourced from Verizon 2022 Data Breach Investigations Report
- Cloud

