by Cody Dumont
January 2, 2020
Organizations cannot begin to fix systemic problems within their security program without first being able to analyze the data collected with a SCAP-compliant vulnerability scanning tool. CIS requires the continuous monitoring of vulnerabilities and identification of unsupported software. Tenable.sc uses active and passive detections methods to bring continuous visibility and provide prioritization actions based on business risk and asset discovery.
The CIS ControlsTM are a prioritized set of actions that collectively form a defense-in-depth set of best practices that mitigate the most common attacks against systems and networks. These controls were developed by IT professionals using operational experiences and generally accepted best practices. This dashboard will focus on Control 3 (Continuous Vulnerability Management) and Control 18 (Application Software Security).
Historically CIS has referred the first six CIS controls as cyber hygiene, which focuses on an organization’s cybersecurity activities. The designation of cyber hygiene brought up the fact that these practices may be difficult for organizations with resource and/or expertise limitations. To address any resource or expertise limitation, CIS now recommends following Implementation Groups (IG) to help prioritize CIS control utilization. There are three IG’s, which describe organization by size. The IG specifies a subset of the controls that have been assessed to have a similar risk profile and resources to implement. The IG’s are also meant to be prioritized in IG order regardless of the IG organization size; for example, organizations should implement Sub-Controls in IG1, followed by IG2 and then IG3. The IG’s are described as organizations with limited resources and cybersecurity expertise (IG1); Organizations with moderate resources (IG2); Organizations with significant resources (IG3).
Control 3 requires organizations to continuously acquire, assess, and take action on new vulnerability information in order to identify and remediate risks, thereby reducing the window of opportunity for attackers. Tenable.sc provides an on-premise solution for organizations to better understand cyber exposure in their network. By facilitating the interactions with patch management solutions, which is required by sub control 3.4 & 3.5, Tenable.sc allows all 3 IG levels to better understand risk and mitigate threats.
For IG2 and IG3, Tenable.sc provides the ability to continuously scan the network using active and passive detection methods. Sub control 3.2 requires active scans to run using valid credentials or agent-based scanning. Tenable.sc provides the strong framework for both options and provides historic trending data to demonstrate long term scanning practices. By maintaining a cumulative and mitigated data set, security analysts are able to better compare current scanning results to past results. Using predictive prioritization analysts are now able to use risk rating processes to better assess risk in the network.
After the data is collected, and risk analysis has begun, one aspect of the analysis is detection of unsupported software. As fast as new software enters the network, this task seems insurmountable. However, Tenable’s research team is continuously detecting unsupported software and creating plugins to address these concerns. Additionally, misconfigurations of encryption systems is also common place. Tenable.sc is able to bring this data together in one place providing risk manages a clear picture as to the current state of their Cyber Exposure program.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Executive.
The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.12.0
- Nessus 8.8.
Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) is the market-defining On-Prem Cyber Exposure Platform. Tenable.sc CV provide the ability to continuously Analyze assets for vulnerabilities and unsupported software. By using active and passive detections Tenable.sc provides customers with a full and complete Cyber Exposure platform for completing an effective Cyber Hygiene program prescribed by CIS Controls framework.
This dashboard contains the following components:
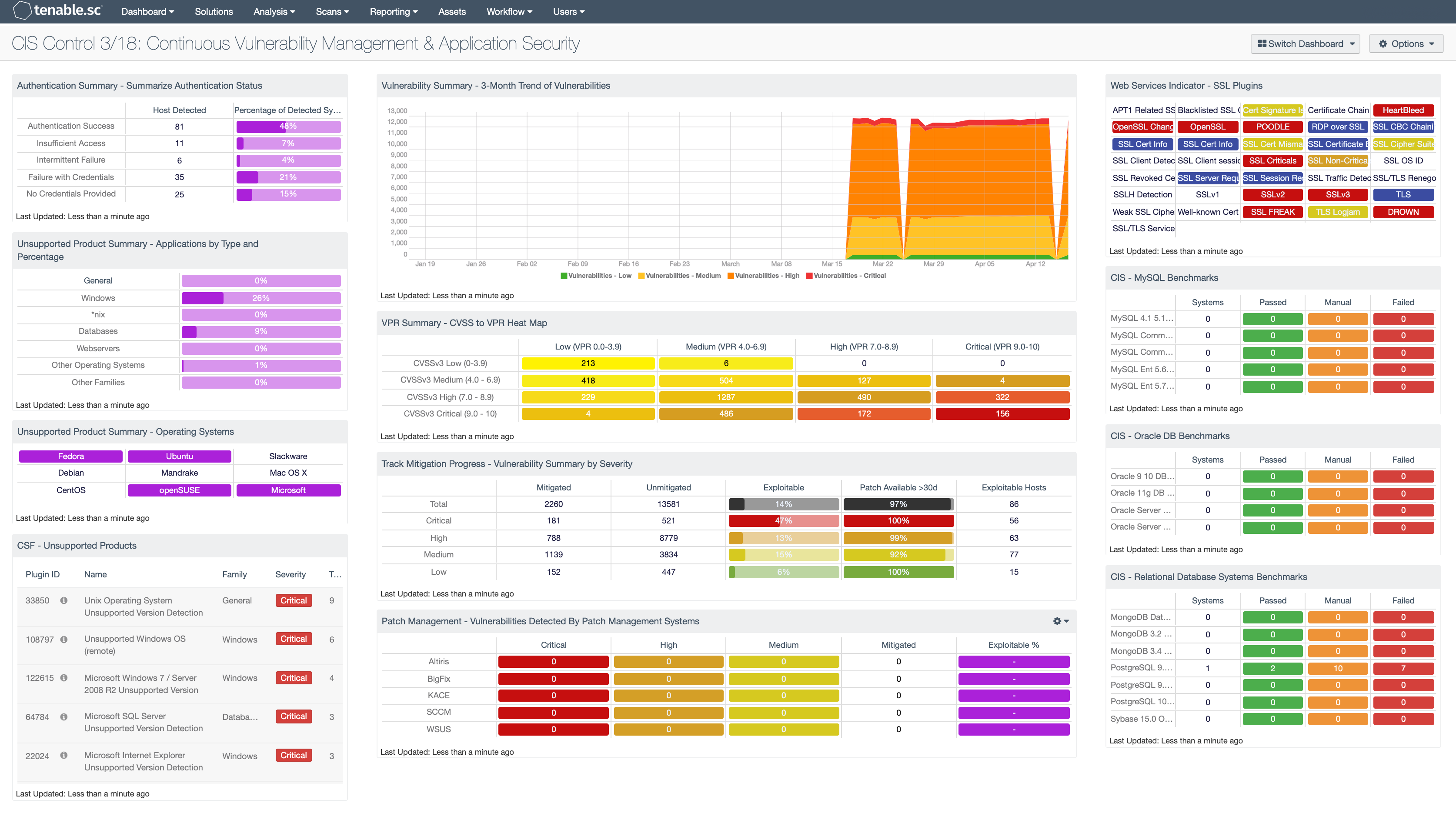
Authentication Summary - Summarize Authentication Status: This matrix provides an overall authentication summary of the systems that have been scanned. The plugins used provide summaries of overall authentication status for the target. A given target should trigger at least one of these plugins. The matrix provides two columns, the “Host Detected” column provides a host count with the respective plugin(s), while the “Percentage of Detected Systems” provides a ratio of total systems scanned. The Total Systems scanned is determined by using the Scan Summary (19506) and the Ping (10180) plugins. The “Percentage of Detected Systems” column, if added together, should total 100% showing all systems scanned with Nessus.
Unsupported Product Summary - Applications by Type and Percentage: This matrix displays the percentage of unsupported applications and operating systems based on plugin family, such as database servers, web servers, Windows, or other operating systems. In this component, the base query uses the plugin family. The percentage is then calculated using the “Unsupported” keyword in the plugin name. The matrix helps illustrate the percentage of unsupported or end-of-life applications within the organization.
Unsupported Product Summary - Operating Systems: This indicator matrix reports on operating systems that are no longer supported. The matrix displays popular operating systems but is easily modified to fit organizational requirements. Plugin ID #33850, with vulnerability text filters that filter for the appropriate operating system name in the plugin output, alert on Unix-based operating systems that are no longer supported. Keyword filters, along with a CPE string for Microsoft, is used to alert on end-of-life Microsoft operating systems by turning the indicator purple when a vulnerable asset is present.
CSF - Unsupported Products: This table displays all unsupported products by name, sorted by severity. Displayed is the plugin ID, product name, plugin family, severity, and the total found. This component identifies unsupported products by filtering on the text unsupported in the vulnerability plugin name. Products and applications that are no longer supported can be serious security risks, as any vulnerabilities will no longer be patched by the vendor.
Vulnerability Summary - 3-Month Trend of Vulnerabilities: This component is a 3-month summary chart tracking unmitigated vulnerabilities of low, medium, high, and critical severity.
VPR Summary - CVSS to VPR Heat Map: This component provides a correlation between CVSSv3 scores and VPR scoring for the vulnerabilities present in the organization. The CVSSv3 scores are the traditional method of analyzing risk, while VPR is a new method based on data science analysis and threat modeling. Each cell is comprised of a combination of cross-mapping of CVSS & VPR scoring. Using a heat map approach, the filters begin in the left upper corner with vulnerabilities with the least risk. Moving to the right and lower down the matrix the colors change darker from yellow to red as the risk levels increase. Customers should mitigate risks in the lower right corners, and then work towards the upper left cells.
Track Mitigation Progress - Vulnerability Summary by Severity: Tenable.sc records when vulnerabilities are discovered, when patches are issued, and when vulnerabilities are mitigated. This component assists in tracking vulnerability mitigations. In the matrix, the row with red is critical severity vulnerability information, the row with orange is high severity, the row with yellow is medium severity, and the row with green is low severity. The Mitigated column displays the number of vulnerabilities that have been moved to the mitigated database. A vulnerability is moved to the mitigated database when the vulnerability is no longer detected by a rescan; the vulnerability is assumed to be remediated. The Unmitigated column displays the number of current vulnerabilities that are not yet remediated and have not been moved to the mitigated database. The Exploitable column displays the percentage of those unmitigated vulnerabilities that are known to be exploitable. The Patch Available column displays the percentage of the unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities that have had a patch available for more than 30 days. Ideally, both of these percentages should be 0%, because all exploitable vulnerabilities and all vulnerabilities with patches available should have been mitigated already. The Exploitable Hosts column displays the number of hosts on the network that have unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities.
Patch Management - Vulnerabilities Detected By Patch Management Systems: This matrix presents an overview of detected vulnerabilities reported by patch management systems. Tenable supports a wide variety of patch management solutions including SCCM, WSUS, IBM BigFix, Dell KACE K1000, and Symantec Altiris. Vulnerabilities are filtered by the Windows: Microsoft Bulletins plugin family, and presents a list of Microsoft vulnerabilities that have been reported by a patch management system. Each column presents the total count of vulnerabilities per severity level, mitigated vulnerabilities, and percentage of exploitable vulnerabilities. Clicking on an indicator will bring up the vulnerability analysis screen to display details on the reported vulnerabilities. In the vulnerability analysis screen, setting the tool to Vulnerability Detail List will display additional details on the vulnerabilities that have been detected by patch management systems. Analysts can use this component to compare the effectiveness of existing patch management systems, and how often systems are being patched.
Web Services Indicator - SSL Plugins: All the plugins that refer to SSL or certificates have been grouped into these indicators. An indicator will not be highlighted if no matches are found; however, if a match is found, the color will change. If all the plugins applied to the indicator have a severity of info or low, then the indicator will turn blue. If any of the selected plugins are medium, high, or critical, the color of the indicator will change to yellow, orange, or red accordingly. However, if there is a mix of info, low, medium, and high, the indicator will be purple. Indicators with a critical severity plugin will always be red.
CIS - MySQL Benchmarks: This matrix component presents a summary of audit checks performed on systems running MySQL. The “Systems” column includes a count of the number of systems scanned against the audit check, and shows whether the operating system, service, or application is installed. Lack of results within the “Systems” column may highlight systems where the object in question is not installed, or the scan needs to be modified. The “Passed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check passed the defined threshold within the CIS benchmark. The “Manual Check” column displays the number of scan results which require a manual review of the audit check to determine a pass or fail. The “Failed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check was outside of the defined parameter in the CIS benchmark. These failed results should be addressed immediately.
CIS - Oracle DB Benchmarks: This matrix component presents a summary of audit checks performed on systems running Oracle DB. The “Systems” column includes a count of the number of systems scanned against the audit check, and shows whether the operating system, service, or application is installed. Lack of results within the “Systems” column may highlight systems where the object in question is not installed, or the scan needs to be modified. The “Passed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check passed the defined threshold within the CIS benchmark. The “Manual Check” column displays the number of scan results which require a manual review of the audit check to determine a pass or fail. The “Failed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check was outside of the defined parameter in the CIS benchmark. These failed results should be addressed immediately.
CIS - Relational Database Systems Benchmarks: This matrix component presents a summary of audit checks performed on systems running Relational Database Systems. The “Systems” column includes a count of the number of systems scanned against the audit check, and shows whether the operating system, service, or application is installed. Lack of results within the “Systems” column may highlight systems where the object in question is not installed, or the scan needs to be modified. The “Passed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check passed the defined threshold within the CIS benchmark. The “Manual Check” column displays the number of scan results which require a manual review of the audit check to determine a pass or fail. The “Failed” column displays the number of scan results where the audit check was outside of the defined parameter in the CIS benchmark. These failed results should be addressed immediately.