by Cody Dumont
July 1, 2020
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) was developed to create a framework to assess an organization's implementation of cybersecurity practices evenly across the defense industrial base. Using NIST 800-53 and NIST 800-171 as the baseline, the primary objective of CMMC is to consolidate the two security catalogs into a single measurable framework. Over the next 5 years, starting in June 2020, organizations that create Government off-the-shelf (GOTS) products, handle Federal Contract Information (FCI), or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) will need to show compliance at 1 of the 5 levels. Only Certified 3rd Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAO) will be able to certify an organization as compliant or not. Security Center provides on-prem solutions for assessing Cyber Exposure practices and maps these practices to known assessment regulations such as NIST, CSF, and others. This dashboard showcases practices from the Asset Management (AM), Risk Management (RM), Security Assessment (CA), Situational Awareness (SA), and System & Information Integrity (SI) domains.
Organizations in the defense industrial base are continuously exposed to an increasing number of vulnerabilities and risks throughout their environments. Based on the DoD’s unique risk tolerance and compliance requirements, risk managers are tasked with fully understanding and documenting vulnerabilities that present the greatest risk. CMMC helps define the actions needed to identify vulnerabilities and assist organizations in responding to these threats in a timely manner.
Risk managers can use the Cyber Exposure Life Cycle to help navigate the CMMC. For example, the first stage is “Discovery” and control AM.4.226 states “Employ a capability to discover and identify systems with specific component attributes (e.g., firmware level, OS type) within your inventory”. Security Center uses active and passive detection methods to identify assets. Once the asset is identified, then Security Center can do more inclusive scans to collect attributes needed for a proper inventory.
The next two stages of the Life Cycle are “Access” and “Analyze”, which closely align to the CA domain, in the two following controls:
- CA.2.158: Periodically assess the security controls in organizational systems to determine if the controls are effective in their application.
- CA.3.161: Monitor security controls on an ongoing basis to ensure the continued effectiveness of the controls.
As the landscape of the network continues to change, the risk manager must not take a set and forget approach to implementing security controls. By implementing Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) Security Technical Implementation Guides (STIGs) or the Center for Internet Security (CIS) benchmarks, the manager can easily use Security Center to monitor for changes to compliance settings. Through a continuously scanning strategy, the search for configuration errors or new vulnerabilities better prepares the organization to respond to active threats and security breaches.
The remaining two steps in the Cyber Exposure Lifecycle are Fix and Measure, which are easily mapped to RM domain, for example:
- RM.2.142: Scan for vulnerabilities in organizational systems and applications periodically and when new vulnerabilities affecting those systems and applications are identified.
- RM.2.143: Remediate vulnerabilities in accordance with risk assessments.
Security Center tracks vulnerabilities as scans are completed, and can report on mitigation efforts. Using two datasets, the Cumulative and Mitigated databases, Security Center tracks the presence of a vulnerability on a system, then on subsequent scans when the vulnerability is removed, the absence of the vulnerability is recorded. In the absence, the vulnerability is moved from the cumulative to the mitigated database. The risk manager can then measure the success of the vulnerability management program and ultimately track the reduction of risk to the organization.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.12.0
- Nessus 8.9.0
- Compliance Data
Security Center is the market-defining On-Prem Cyber Exposure Platform. Security Center provides the ability to continuously Assess an organization’s adherence to best practice configuration baselines. Security Center provides customers with a full and complete Cyber Exposure platform for completing an effective cybersecurity practices prescribed by CMMC standard.
Components
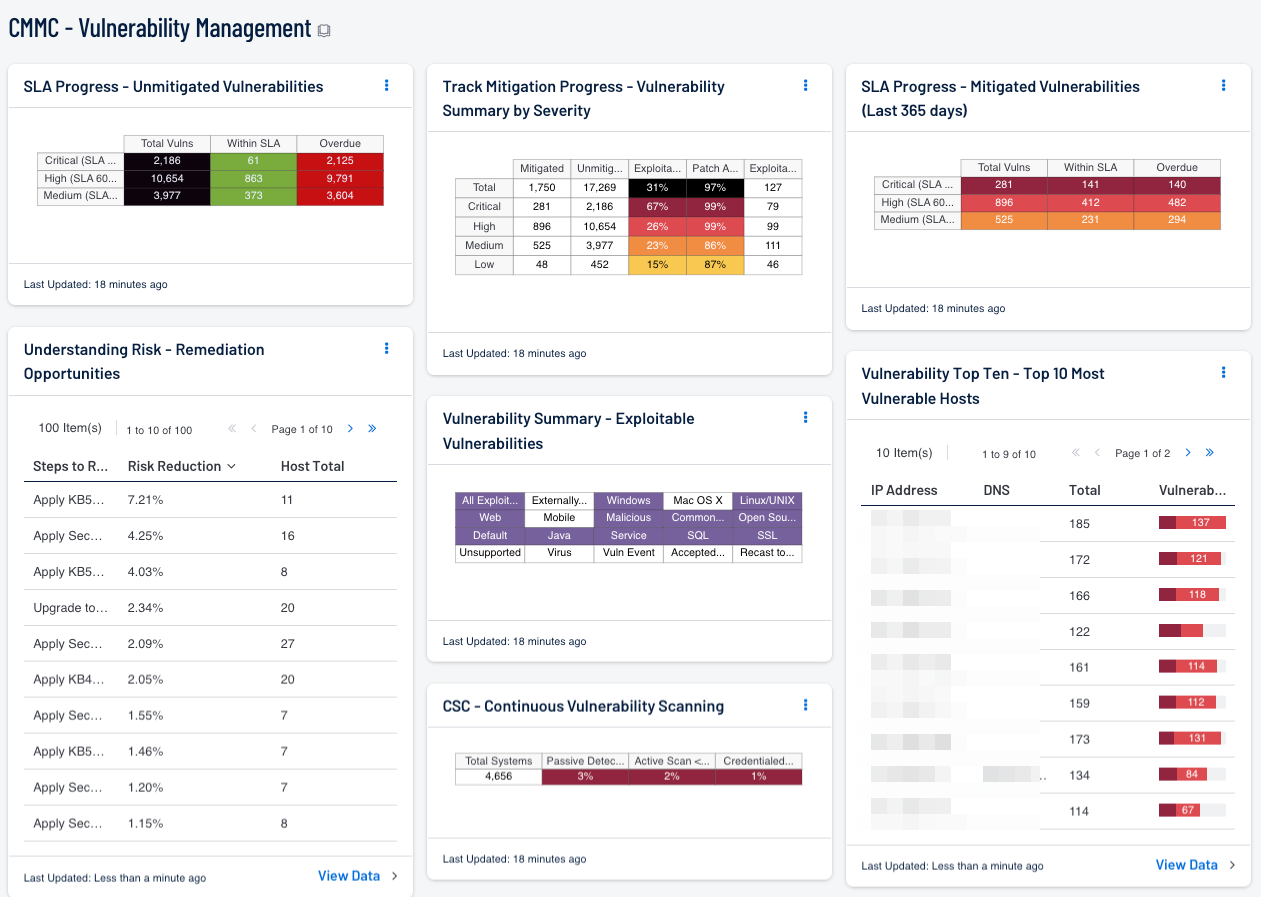
SLA Progress - Unmitigated Vulnerabilities: The matrix provides a summary of vulnerabilities based on the CVSS score and the SLA of 30, 60, 90 days. Each of the three rows are based on the CVSS severity from Medium to Critical. The three columns illustrate the count of vulnerabilities across all systems. The black cells are the count of vulnerabilities, with green meaning newly discovered and are within the prescribed SLA, while the red count are vulnerabilities that have been detected on the network for more than the allotted mitigation time.
Understanding Risk - Remediation Opportunities: This table displays the top remediations for the network. For each remediation, the risk reduction for the network if the remediation is implemented is shown, along with the number of hosts affected. The table is sorted so that the highest risk reduction is at the top. Implementing the remediations will decrease the overall vulnerability of the network. Adding filters to the component, such as filtering on only critical severity vulnerabilities or filtering on a specific asset group, can narrow the focus of the component, giving remediation opportunities in specific areas.
Track Mitigation Progress - Vulnerability Summary by Severity: Security Center records when vulnerabilities are discovered, when patches are issued, and when vulnerabilities are mitigated. This component assists in tracking vulnerability mitigations. In the matrix, the row with red is critical severity vulnerability information, the row with orange is high severity, the row with yellow is medium severity, and the row with green is low severity. The Mitigated column displays the number of vulnerabilities that have been moved to the mitigated database. A vulnerability is moved to the mitigated database when the vulnerability is no longer detected by a rescan; the vulnerability is assumed to be remediated. The Unmitigated column displays the number of current vulnerabilities that are not yet remediated and have not been moved to the mitigated database. The Exploitable column displays the percentage of those unmitigated vulnerabilities that are known to be exploitable. The Patch Available column displays the percentage of the unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities that have had a patch available for more than 30 days. Ideally, both of these percentages should be 0%, because all exploitable vulnerabilities and all vulnerabilities with patches available should have been mitigated already. The Exploitable Hosts column displays the number of hosts on the network that have unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Summary - Exploitable Vulnerabilities: This matrix displays warning indicators for exploitable vulnerabilities actively and passively detected on the network, including vulnerabilities by OS, web vulnerabilities, application vulnerabilities, and vulnerabilities by keywords such as "Java" and "unsupported". Exploitable vulnerabilities that are externally accessible (i.e., accessible from hosts outside of the configured network address range) are very dangerous and must be remediated as soon as possible. Exploitable vulnerabilities that have been marked as accepted risks or recast to Informational within Security Center are also noted; these vulnerabilities should likely be re-evaluated. Clicking on a highlighted indicator will bring up the vulnerability analysis screen to display details for the vulnerabilities and allow further investigation. In the analysis screen, setting the tool to IP Summary will display the systems on which the vulnerabilities are present. Setting the tool to Vulnerability Details will display the full details for each vulnerability, including a description, the solution to fix the vulnerability, and in some cases, links to more information.
CSC - Continuous Vulnerability Scanning: This matrix assists in monitoring the vulnerability detection and scanning performed by the Tenable Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) and Tenable Nessus. Presented are the percentages of total systems that have had recent passive vulnerability detections, active vulnerability scans, and credentialed scans. This information highlights detection coverage and whether vulnerability scans are being regularly executed. The timeframes may be altered to fit organizational requirements.
SLA Progress - Mitigated Vulnerabilities (Last 365 days): The matrix provides a summary of the mitigated vulnerabilities discovered over the past 365 days. The rows depict the time required to mitigate (30, 60, 90 days) and the CVSS severity level. The three columns illustrate the count of vulnerabilities across all systems. To provide more focus to an asset group, the component can be installed with focus option set accordingly. The black cells are the count of vulnerabilities, with green meaning newly discovered and are within the prescribed SLA, while the red count are vulnerabilities that have been detected on the network for more than the allotted mitigation time.
Vulnerability Top Ten - Top 10 Most Vulnerable Hosts: This component shows the top ten hosts with exploitable vulnerabilities of high or critical severity. Editing the filters in the component and changing the tool from IP Summary to Class C Summary or Port Summary can give information on exploitable vulnerabilities per subnet or per port, respectively.