by Cody Dumont
February 26, 2016
As organizations continue to evolve, wireless technologies are being integrated into existing networks to support employee mobility needs. Misconfigured wireless devices can pose a security risk, and leave a network vulnerable to attack by unauthorized users and devices. This dashboard aligns with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) PR.PT-4 subcategory, which utilizes both active and passive methods to identify wireless access points and vulnerabilities found within a network.
The CSF provides guidance based on existing standards, guidelines, and practices that can be tailored to specific organizational needs. This dashboard utilizes the Protective Technology subcategory within the CSF Protect category, which assists in ensuring that security of, and access to, wireless systems are controlled.
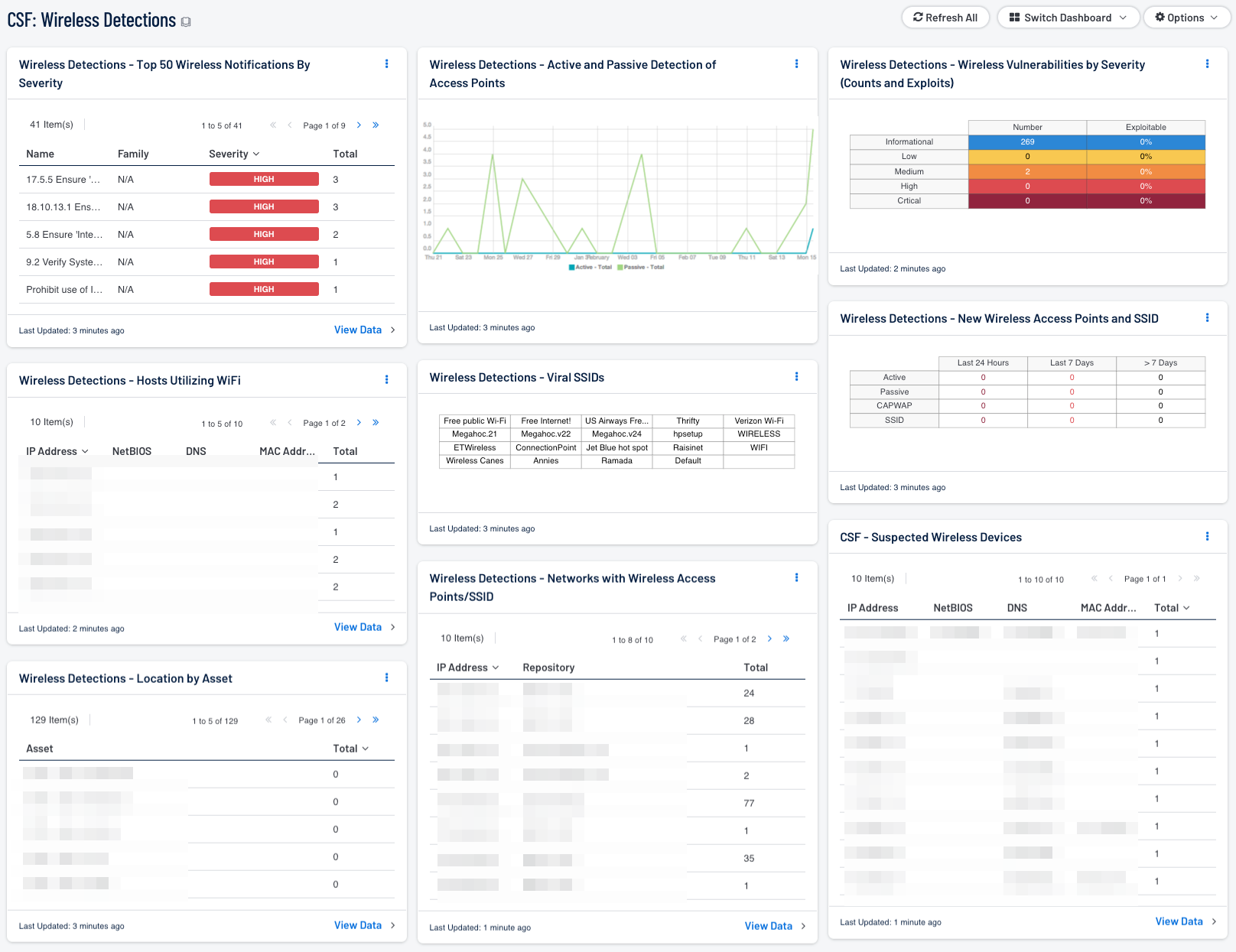
This dashboard will assist in providing an inventory of wireless access points, events from wireless devices, and wireless vulnerabilities. An important aspect of detecting wireless devices is identifying access points by their Service Set Identifier (SSID). Nessus plugins are utilized to detect both wireless access points and SSID’s with a network. Tables are sorted by Class C address space and detected hosts using wireless. Trend chart data reflects both active and passive wireless access point detections, which could identify new or rogue wireless device connections. Several components display both active and passive wireless access points, along with wireless vulnerabilities. This information can assist the analyst in quickly determining the host count, severity level, and if any of the detections are exploitable.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.2.0
- Nessus 8.5.1
- PVS 5.9.0
Tenable Security Center is the market-defining continuous network monitoring platform. Security Center includes active vulnerability detection with Nessus and passive vulnerability detection with Tenable’s Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) Using Security Center, an organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of wireless events and devices across the network.
The following components are included in this dashboard:
- Wireless Detections - Active and Passive Detection of Access Points: The Active and Passive Detection of Access Points chart displays a trend over the last 25 days of all wireless access points detected actively or passively. Wireless devices are identified for both passive and active detections over a 24-hour period, trending for 25 days. Spikes in trend activity for active detections usually depict when active Nessus scanning on the network has occurred, while passive detections occur immediately when devices are detected by Tenable’s Passive Vulnerability Scanner.
- Wireless Detections - Networks with Wireless Access Points/SSID: The Networks with Wireless Access Points/SSID table displays detections by count of Wireless Access Points detected by active scanning, and presents the count by Class C address space. The table quickly allows the analyst to determine the physical counts of wireless access points by Class C address space within the organization. This allows the analyst to determine if any access points are outside of any specified address space. This table allows for immediate drill down for a more detailed view.
- Wireless Detections - Location by Asset: The Location by Asset table lists Nessus plugin 25197 – Windows Wireless SSID Detection result totals by Security Center asset names. In Security Center, hosts can be grouped by a large number of criteria including network location. To use the table efficiently, it would be prudent to ensure that asset names representing network locations include some indicator if they are within a known WLAN network range.
- Wireless Detections - Wireless Vulnerabilities by Severity (Counts and Exploits): The Wireless Vulnerabilities by Severity matrix component presents a severity and vulnerability summary that allows the analyst to quickly determine the physical counts of detections by severity and if any of the detections are exploitable.
- Wireless Detections - New Wireless Access Points and SSID: The New Wireless Access Points and SSID indicates on triggers from active and passive detection type plugins, by plugin ID, and vulnerability text. Data displayed displays the number of wireless access points detected over time. Indications are filtered by time, into columns for the last 24 hours, last 7 days and last 30 days. If no indication is present for the specified time period, zero is shown. If an alert is present, the indication changes to the number of access points discovered. The analyst may click on the indicator to retrieve further details on the number of access points discovered during the scan.
- Wireless Detections - Viral SSIDs: This Viral SSIDs matrix derives its list of interesting SSIDs from an article published in 2008 titled: Study shows viral SSIDs could be creating a massive wireless botnet. Reading about ad hoc wireless networks and recommended Windows related configuration settings is very interesting and the topic is made even more interesting by attempting to find the relevant settings mentioned in published hardening guides. The matrix is a convenient way to provide a grouping of interesting SSIDs as reported by plugin 25197. After a wireless site survey, you may wish to repurpose the matrix to list other interesting SSIDs not broadcast by your organization. Please take into consideration that the SSID filtering performed by the dashboard components is case insensitive.
- Wireless Detections - Hosts Utilizing WiFi: The Hosts Utilizing WiFi table component utilizes data from Nessus plugin 24272, Network Interface Enumeration, and filters for the term “wireless” to display hosts that have active wireless interfaces. Plugin output displays the network interface details, including the MAC address and IP address.
- Wireless Detections - Top 50 Wireless Notifications By Severity: The Top 50 Wireless Notifications By Severity table component displays a list of the Top 50 most prevalent detections using the vulnerability summary tool, sorted by total. The table presents the analyst with a method to view detections in a readable format. Detections that are the most common are listed at the top of the table and are sorted in a descending order. The plugin ID, name, family and severity rating are also displayed for the analyst. Detections are listed by using a filter for the “wireless” keyword contained within the vulnerability text. This may or may not represent an actual vulnerability associated with a wireless AP, but will represent any possible wireless related vulnerability.
- CSF - Suspected Wireless Devices: Along with wireless devices, many stand-along devices today include wireless access capabilities such as printers, digital cameras, and more. This component presents detected suspected wireless devices on hosts within a network. Analysts can drill down to obtain additional information on the suspected wireless device, and determine whether the device is authorized for use on the network.