by Stephanie Dunn
June 20, 2016
Assets within an organization are moving, joining, and leaving a network on a daily basis, which can be difficult to manage properly. Organizations that have an accurate asset management system can gain complete visibility on what devices are in use, and what software is installed on the network. The ISO/IEC27000 Asset Management dashboard can assist the organization in providing an accurate asset inventory data, which can aid in minimizing potential threats, manage software licensing, and ensure compliance.
The ISO/IEC 27002:2013 framework is a global security standard that provides best practice solutions in support of the controls found in Annex A of ISO/IEC 27001:2013. The framework establishes guidelines and general principles for initiating, implementing, maintaining, and improving information security management systems (ISMS). Each security controls and objectives provided within the standard can be tailored to specific business and regulatory objectives, and assist with maintaining overall compliance. This dashboard focuses on the ISO/IEC 27002 8.1.1 and 8.1.2 controls that will assist organizations in identifying assets, asset ownership, and aid in maintaining an accurate, and up to date asset inventory.
As organizations continue to see an increase in employee mobility needs, additional devices such as tablets, mobile phones, and laptops will routinely traverse the network. Maintaining an up-to-date hardware asset inventory will allow organizations to readily identify authorized assets, minimize security risks, and manage costs effectively. Identifying what software assets are installed can aid in managing software licenses, and help to reduce additional costs to an organization. To ensure compliance, the analyst will need to scan, monitor, and identify new and existing assets on a continuous basis.
This dashboard displays various types of hardware assets on a network, including mobile devices, infrastructure devices, and wireless access points. Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) has the ability to detect hardware and software assets by Nessus and NNM. The analyst will be able to identify mobile devices that are scanned by NNM, and mobile devices that are managed by MDM servers. Having an accurate hardware inventory will aid in managing, disposing, and replacing systems effectively. Organizations will be able to track operating systems, licensed software applications, and unsupported products on a network. In addition, analysts can use this information to determine when operating system upgrades are needed, software on each host, track software purchases, and maintain license compliance. The components within this dashboard will provide clear visibility into existing network assets. Analysts can use this information to remediate issues with any unauthorized assets, unsupported software, or malicious hosts.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.3.2
- Nessus 8.5.1
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) provides continuous network monitoring, vulnerability identification, risk reduction, and compliance monitoring. Nessus is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities, and new types of regulatory compliance configuration audits. NNM and Nessus both have the capability to discover operating systems, software, network devices, hypervisors, databases, tablets, phones, servers, and other critical assets. Tenable.sc CV allows for the most comprehensive and integrated view of network health.
This dashboard contains the following components:
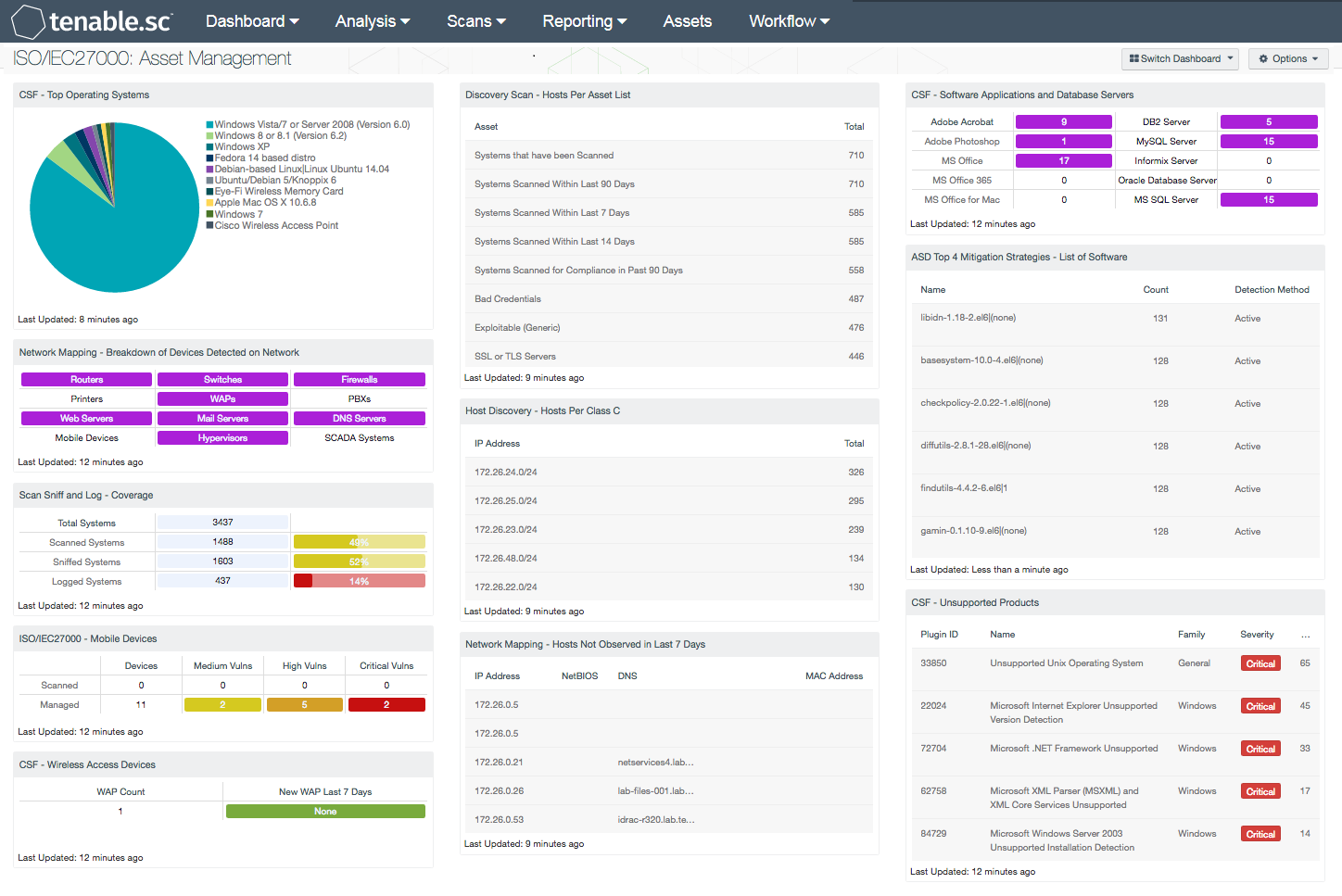
- CSF - Top Operating Systems: This component displays a chart of the top operating systems (OS) detected within a network. The list is organized starting with the highest number of systems by OS version at the top. Detected systems such as physical, virtual, mobile, and infrastructure OS versions are included. Information within this list can assist the analyst in identify existing operating systems for upgrade and inventory purposes.
- Network Mapping - Breakdown of Devices Detected on Network: This matrix presents a breakdown of detected network systems by type. A purple indicator denotes that systems of that type were detected; clicking on the indicator will bring up information on each of the detected systems, including IP address and MAC address. This information can assist an organization in maintaining an accurate inventory and detecting any unauthorized systems. The type of the network system is determined either based on its operating system (OS) or by the actively or passively detected vulnerabilities it has. Indicators are included for routers, switches, firewalls, printers, wireless access points (WAPs), PBXs, web servers, mail servers (IMAP, POP, and SMTP servers, as well as other specific servers such as Microsoft Exchange), DNS servers, mobile devices, hypervisors (virtual machines), and SCADA systems.
- Scan Sniff and Log - Coverage: The Scan Sniff and Log – Coverage matrix presents the total number of systems, along with the total number of scanned, sniffed, or logged systems and corresponding percentages. Scanned systems are detected by Nessus through network scans performed. Sniffed systems are discovered passively through NNM. Logged systems are detected through LCE, however some IP addresses may or may not be in use on the network and should be reviewed further. The data displayed within this table includes the detected IP address and DNS name of the newly detected host.
- ISO/IEC27000 - Mobile Devices: This component presents both scanned and managed mobile devices on a network. Scanned mobile devices are detected using NNM, and include mobile devices that are not managed by an MDM Server. The data displays the number of detected scanned and managed mobile devices, along with associated vulnerabilities by severity level. If no indication is present for the specified severity or count, zero is shown. The analyst may click on the indicator to retrieve further details on specific mobile devices.
- CSC - Wireless Access Devices: The Wireless Access Devices component uses active plugins from Nessus and passive plugins from NNM to locate wireless access devices on a network. Information presented within this matrix will alert analysts to both new and existing wireless access points across the enterprise.
- Discovery Scan - Hosts Per Asset List: The 'Hosts Per Asset List' table component lists the live host counts distributed across Tenable.sc 4 assets. In the screen shot, example network locations with their labels have been uploaded into Tenable.sc 4 and represent physical locations. A retail store could upload their store locations and corresponding network CIDRs.
- Discovery Scan - Hosts Per Class C: The 'Hosts Per Class C' table component displays live hosts across /24 network blocks. The table is sorted so the highest number of systems is presented at the top. A dashboard user can modify the component to report across /16 or /8 network blocks. If more sophisticated VLSM network division is required, it is recommended to leverage the Hosts Per Asset List table and upload the network ranges required with appropriate labels.
- Network Mapping - Hosts Not Observed in Last 7 Days: This table lists those systems that were last passively observed on the network more than seven days ago. Tenable's NNM detects hosts on the network and records their last observed date. This table presents host information for any hosts whose last observed date is more than seven days ago. Discovering hosts that have stopped talking on the network can assist an organization in maintaining an accurate inventory and detecting unusual activity.
- CSF - Software Applications and Database Servers: This component displays a matrix of detected software programs and database servers that are commonly used within organizations. This component can assist the organization in tracking software licenses, compliance and inventory purposes. Each matrix utilizes a combination of plugins and CPEs to detect specific software installations. If a software application or database server is detected on the network, the indicator will be highlighted in purple along with the total number of installations by count. Although the range of software applications and database servers can vary among organizations, this matrix can be modified to fit business requirements.
- ASD Top 4 Mitigation Strategies - List of Software: The foundation of application whitelisting is knowing what applications are installed within an organization. Tenable.sc CV can collect information about installed applications using the List of Software tool, and by collecting logs from several sources such as workstations, servers, and enterprise whitelist applications. This component provides a detailed list of software currently discovered on the network. The best practice with this component is to create several copies of the component, and apply an asset or subnet to each component. Modifying the filters in this manner will provide the organization with the details for installed software for each targeted segment of the network.
- CSF - Unsupported Products: This table displays all unsupported products by name, sorted by severity. Displayed is the plugin ID, product name, plugin family, severity, and the total found. This component identifies unsupported products by filtering on the text ”unsupported” in the vulnerability plugin name. Products and applications that are no longer supported can be serious security risks, as any vulnerabilities will no longer be patched by the vendor.