Microsoft’s February 2024 Patch Tuesday Addresses 73 CVEs (CVE-2024-21351, CVE-2024-21412)

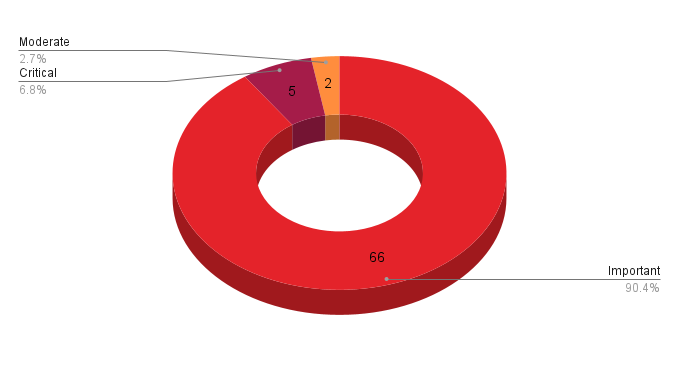
- 5Critical
- 66Important
- 2Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft addresses 73 CVEs, including three zero-day vulnerabilities that were exploited in the wild.
Update February 15: The blog has been updated for CVE-2024-21413, which Microsoft had mistakenly added the "exploitation detected" tag in their advisory for a short period on February 14. In addition, CVE-2024-21410 has been updated to indicate that is has been exploited.
Microsoft patched 73 CVEs in its February Patch Tuesday release, with five rated critical, 66 rated as important and two rated as moderate.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- .NET
- Azure Active Directory
- Azure Connected Machine Agent
- Azure DevOps
- Azure File Sync
- Azure Site Recovery
- Azure Stack
- Internet Shortcut Files
- Microsoft ActiveX
- Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office OneNote
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Microsoft Office Word
- Microsoft Teams for Android
- Microsoft WDAC ODBC Driver
- Microsoft WDAC OLE DB provider for SQL
- Microsoft Windows
- Microsoft Windows DNS
- Role: DNS Server
- SQL Server
- Skype for Business
- Trusted Compute Base
- Windows Hyper-V
- Windows Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
- Windows Kernel
- Windows LDAP - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- Windows Message Queuing
- Windows OLE
- Windows SmartScreen
- Windows USB Serial Driver
- Windows Win32K - ICOMP
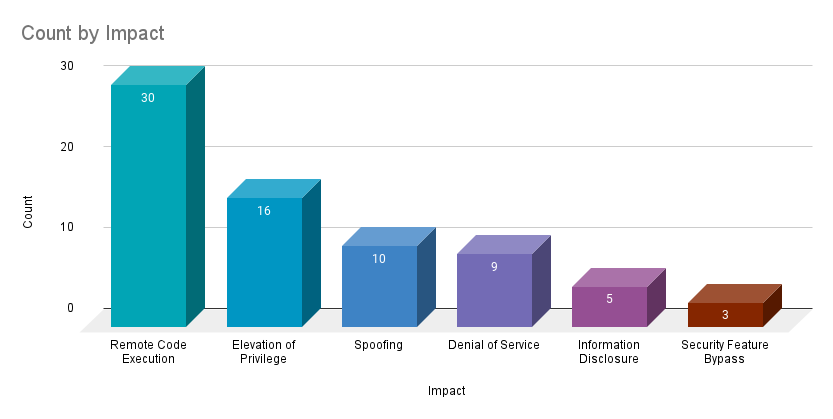
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 41.1% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 21.9%.
CVE-2024-21351 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21351 is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Windows SmartScreen. It was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 7.6 and is rated moderate. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by convincing a target to open a malicious file. Successful exploitation would bypass SmartScreen security features. According to Microsoft, this vulnerability has been exploited in the wild as a zero-day, though no specific details about exploitation were available at the time this blog was published.
Since 2022, there have been five Windows SmartScreen vulnerabilities disclosed across Patch Tuesday. All five have been exploited in the wild as zero-days.
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 | Severity | Patch Tuesday |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2022-44698 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 5.4 | Moderate | December 2022 |
| CVE-2023-24880 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 4.4 | Moderate | March 2023 |
| CVE-2023-32049 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 8.8 | Important | July 2023 |
| CVE-2023-36025 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 8.8 | Important | November 2023 |
CVE-2024-21412 | Internet Shortcut Files Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21412 is a security feature bypass in Internet Shortcut Files. It was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.1 and is rated important. Exploitation of this flaw requires an attacker to convince their intended target to open a malicious Internet Shortcut File using social engineering.
According to Microsoft, this vulnerability was exploited in the wild as a zero-day. It was disclosed to Microsoft by several researchers including Pter Girnus of Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative, Dima Lenz and Vlad Stolyarov of Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) and dwbzn with Aura Information Security. No specific details about this zero-day vulnerability was available at the time of the February Patch Tuesday release.
CVE-2024-21410 | Microsoft Exchange Server Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21410 is a critical EoP vulnerability with a CVSSv3 score of 9.8 and is rated “Exploitation More Likely” according to the Microsoft Exploitability Index. Successful exploitation of this flaw would allow an attacker to relay a New Technology LAN Manager Version 2 (NTLMv2) hash against a vulnerable server. NTLM hashes could be abused in NTLM relay or pass-the-hash attacks to further an attacker's foothold into an organization. On February 14, Microsoft updated their advisory to note that this vulnerability has been exploited, making this the third zero-day vulnerability for this months Patch Tuesday release.
According to Microsoft, Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update 14 and prior did not enable NTLM credentials Relay Protections by default. Microsoft’s advisory provides a link to a script to enable the protection and recommends installing the latest cumulative update, even if the script to enable the NTLM credentials Relay Protections has been run.
Microsoft Exchange Server has been a favored target by threat actors and ransomware groups alike, with multiple vulnerabilities having been exploited in-the-wild and encompassing some of the top routinely exploited vulnerabilities of 2022. Vulnerabilities like ProxyLogon (CVE-2021-26855), ProxyShell (CVE-2021-34473, CVE-2021-34523 and CVE-2021-31207) and ProxyNotShell (CVE-2022-41040 and CVE-2022-41082) have been heavily used by threat actors and have been discussed in multiple blog posts by our team, including being featured in our 2021 and 2022 Threat Landscape Reports.
At the time this blog was published, no known exploitation has been observed for CVE-2024-21410. However with the update to the advisory on February 14 to indicate that exploitation has been detected, this is a vulnerability to remediate as quickly as possible.
CVE-2024-21378 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21378 is a RCE vulnerability affecting Microsoft Outlook. This flaw is rated as “Exploitation More Likely” and was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.0. In order to exploit this flaw, an attacker would need to be authenticated with LAN-access and have a valid login for an Exchange user. If the attacker meets those requirements, they would then have to send their maliciously crafted file to a user and entice them to open it. According to Microsoft, the preview pane is an attack vector, meaning that simply previewing a specially crafted file can cause the exploit to trigger.
CVE-2024-21413 | Microsoft Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21413 is a RCE vulnerability affecting Microsoft Outlook. This flaw was originally rated as “Exploitation Less Likely” when released by Microsoft on February 13. However on February 14, Microsoft updated the advisory to note that this RCE had been exploited in the wild as a zero-day. Later on the same day, Microsoft updated the advisory again, removing the "Exploitation Detected" tag and revising the advisory to reflect the exploitability as "Exploitation Unlikely."
Haifei Li at Check Point Research was credited with the discovery of the vulnerability and a blog post from Check Point provides details on their discovery, including the name they refer to the bug as, #MonikerLink. We recommend reviewing their blog post for technical details and applying the patch as soon as possible.
CVE-2024-21338, CVE-2024-21345 and CVE-2024-21371 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-21338, CVE-2024-21345 and CVE-2024-21371 are EoP vulnerabilities affecting the Windows Kernel. The vulnerabilities were each given different CVSSv3 scores varying from 8.8 for CVE-2024-21345 to 7.0 for CVE-2024-21371 with each rated as “Exploitation More Likely.” An attacker could exploit these vulnerabilities as part of post-compromise activity to elevate privileges to SYSTEM.
In addition to these EoP vulnerabilities, three additional Windows Kernel vulnerabilities were patched this month:
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2024-21340 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability | 4.6 |
| CVE-2024-21341 | Windows Kernel Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 6.8 |
| CVE-2024-21362 | Windows Kernel Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | 5.5 |
Tenable Solutions
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s February 2024 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
For more specific guidance on best practices for vulnerability assessments, please refer to our blog post on How to Perform Efficient Vulnerability Assessments with Tenable.
Change Log
Get more information
- Microsoft's February 2024 Security Updates
- Tenable plugins for Microsoft February 2024 Patch Tuesday Security Updates
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management
