Microsoft’s June 2022 Patch Tuesday Addresses 55 CVEs (CVE-2022-30190)

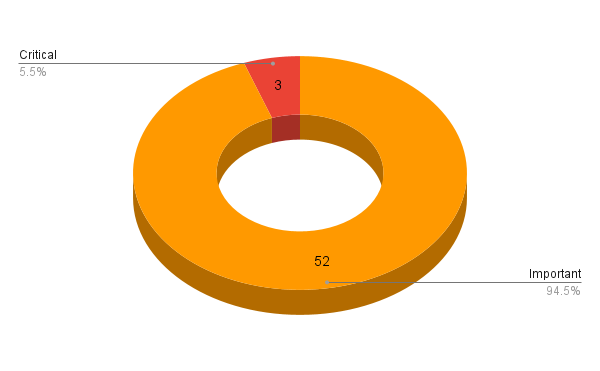
Microsoft addresses 55 CVEs in its June 2022 Patch Tuesday release, including three critical flaws.
- 3Critical
- 52Important
- 0Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft patched 55 CVEs in its June 2022 Patch Tuesday release, with three rated as critical, 52 rated as important.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- .NET and Visual Studio
- Azure OMI
- Azure Real Time Operating System
- Azure Service Fabric Container
- Intel
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Windows ALPC
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library
- Remote Volume Shadow Copy Service (RVSS)
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- SQL Server
- Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
- Windows App Store
- Windows Autopilot
- Windows Container Isolation FS Filter Driver
- Windows Container Manager Service
- Windows Defender
- Windows Encrypting File System (EFS)
- Windows File History Service
- Windows Installer
- Windows iSCSI
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows LDAP - Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem Service
- Windows Media
- Windows Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Windows Network File System
- Windows PowerShell
- Windows SMB
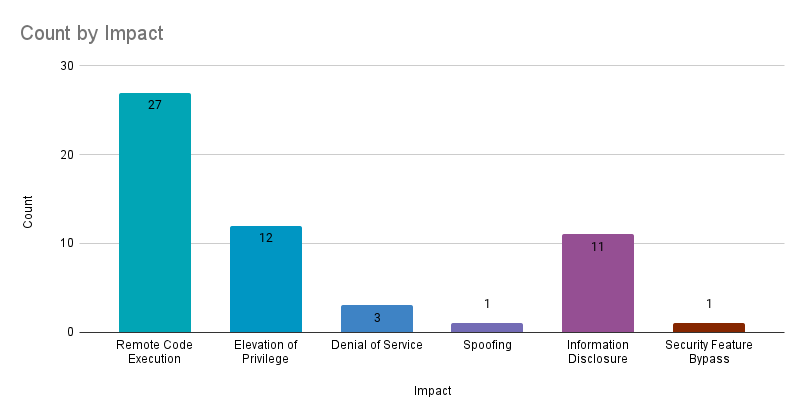
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 49.1% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 21.8%.
CVE-2022-30136 | Windows Network File System Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-30136 is a RCE vulnerability in the network file system (NFS) that can be exploited by an unauthenticated attacker using a specially crafted call to a NFS service. The vulnerability received a 9.8 CVSSv3 score and Microsoft rated this as “Exploitation More Likely” according to its Exploitability Index. The advisory notes that NFS versions 2.0 and 3.0 are not affected and administrators can disable NFS version 4.1 to mitigate this flaw. Disabling NFSv4.1 could have adverse impacts, so organizations should carefully consider this step before adopting it. Microsoft does note that this is only a temporary mitigation option, organizations should apply the patch as soon as possible. The advisory also provides a warning that you should not disable NFSv4.1 unless you have installed the May 2022 Windows security updates, specifically the updates addressing CVE-2022-26937.
Both CVE-2022-30136 and CVE-2022-26937 are credited to Yuki Chen, a prolific researcher with Cyber KunLun who has been credited with discovering nine vulnerabilities in Microsoft products in June 2022.
CVE-2022-30160 | Windows Advanced Local Procedure Call Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2022-30160 is an EoP vulnerability affecting the advanced local procedure call (ALPC), a message-passing mechanism for internal operating system communications. With a CVSSv3 score of 7.8, this vulnerability can be exploited by a local, authenticated attacker. Researcher Jarvis_1oop is credited with discovering this flaw, which was rated as“Exploitation More Likely.” patches are available for all supported Windows variants including Windows Server Core installations.
CVE-2022-30147 | Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2022-30147 is an EoP vulnerability affecting the Windows Installer. The flaw received a 7.8 CVSSv3 score and can be exploited by a local, authenticated attacker. Microsoft’s exploitability assessment rates this vulnerability as “Exploitation More Likely” and patches are available for all supported Windows variants including Windows Server Core Installations. This vulnerability was an internal discovery at Microsoft credited to Levi Broderick with Microsoft and Andrew Ruddick.
Seven Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities in Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
This month Microsoft patched seven vulnerabilities in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
- CVE-2022-30139
- CVE-2022-30141
- CVE-2022-30143
- CVE-2022-30146
- CVE-2022-30149
- CVE-2022-30153
- CVE-2022-30161
Two of the CVEs, CVE-2022-30153 and CVE-2022-30161 received CVSSv3 scores of 8.8, CVE-2022-30141 was scored at 8.1, and the remainder of the flaws each were scored at 7.5. Microsoft has rated all of these vulnerabilities as “Exploitation Less Likely.” The vulnerability descriptions for CVE-2022-30139, CVE-2022-30141 and CVE-2022-30143 provide the same caveat that the vulnerability only exists if the “MaxReceiveBuffer” LDAP policy is configured to a higher value than the default value (i.e. a higher maximum number of threads LDAP requests can contain per processor). A system with the default value for the policy would not be affected. In the case of both CVE-2022-30139 and CVE-2022-30141, no user interaction is required, however an attacker must “prepare the target environment to improve exploit reliability.” The remainder of the CVEs all require some form of user interaction in order to exploit the vulnerability.
Vulnerabilities not present in release notes
While no release notes or official documentation from Microsoft have been released, Tenable Research has responsibly disclosed two vulnerabilities to Microsoft. The vulnerabilities found in Microsoft's Azure Synapse Analytics were found by Tenable Researcher Jimi Sebree. These flaws allow a user to escalate privileges to that of the root user within the underlying Apache Spark virtual machines, or to poison the hosts file of all nodes in an Apache Spark pool. The keys, secrets and services accessible via these vulnerabilities have traditionally allowed further lateral movement and compromise of Microsoft-owned infrastructure, which could potentially lead to a compromise of other customers’ data as we’ve seen in other research reports. The privilege escalation vulnerability has been patched and no action is required for Azure Synapse Analytics users. You can read more about these vulnerabilities in the Tenable Blog and a detailed write up can be found on our technical blog.
CVE-2022-30190 | Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-30190, also known as “Follina” — the RCE vulnerability in the Microsoft Windows Support Diagnostic Tool that was disclosed in late May and exploited in the wild — has now received patches for affected Windows systems. While Microsoft had provided mitigation guidance in an advisory on May 30, patches were not released until June 14.
Internet Explorer 11 End Of Support
On Wednesday June 15, support for Internet Explorer (IE) 11 will end for certain versions of WIndows 10. Microsoft recommends switching to Microsoft Edge and notes that IE 11 is the last major version for Internet Explorer. Tenable customers can utilize Plugin ID 22024 - Microsoft Internet Explorer Unsupported Version Detection to identify systems that have an unsupported version of IE. An update to the plugin will be released on June 15 to account for these updates from Microsoft.
Tenable Solutions
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced scan, in the plugins tab, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains June 2022.
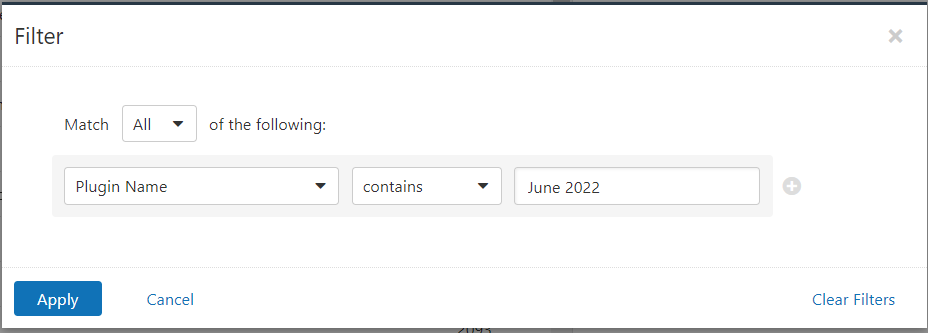
With that filter set, click the plugin families to the left and enable each plugin that appears on the right side. Note: If your families on the left say Enabled, then all the plugins in that family are set. Disable the whole family before selecting the individual plugins for this scan. Here’s an example from Tenable.io:
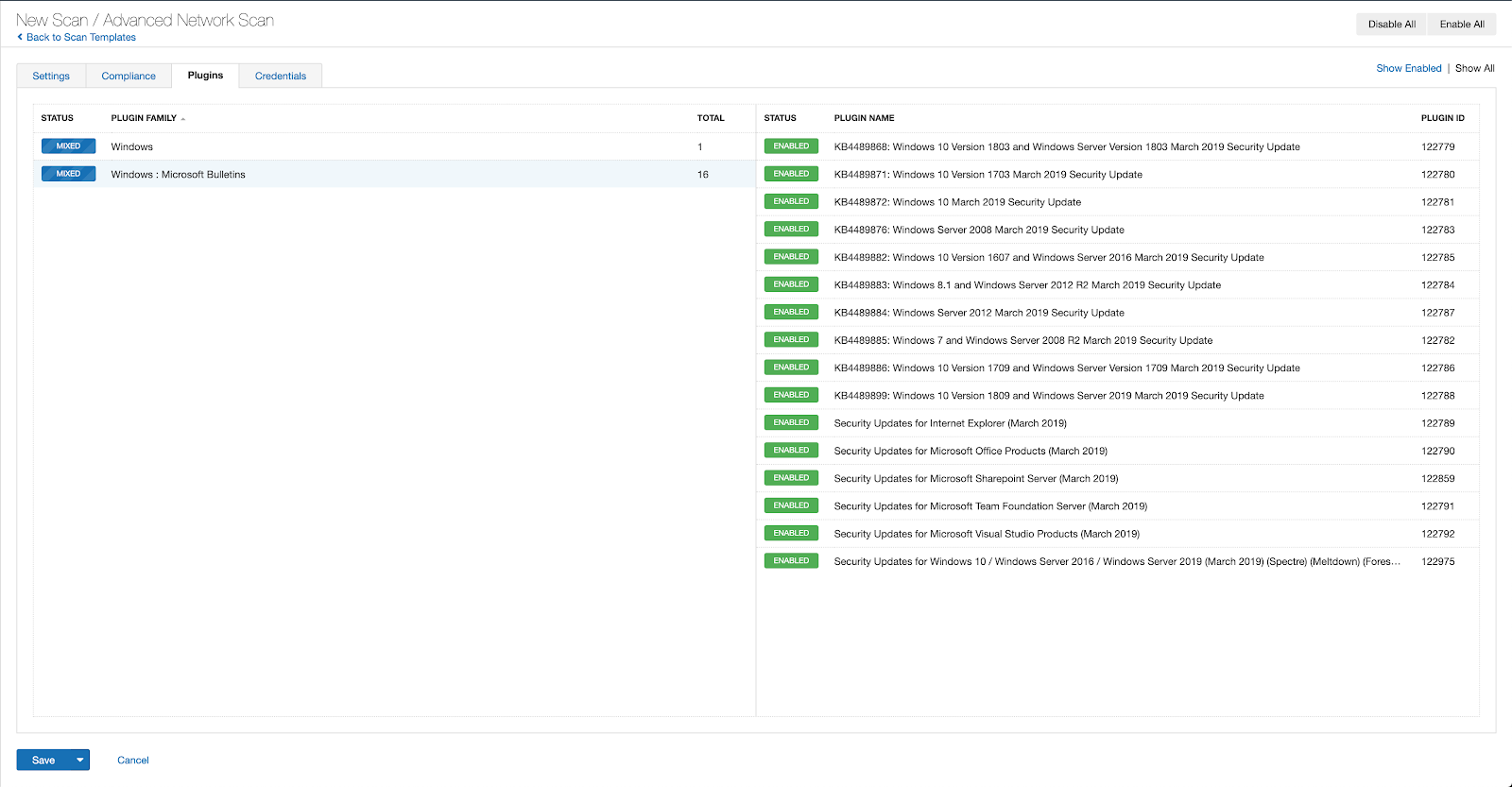
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s June 2022 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
Get more information
- Microsoft's June 2022 Security Updates
- Tenable plugins for Microsoft June 2022 Patch Tuesday Security Updates
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.
- Vulnerability Management
