by Cody Dumont
February 26, 2016
As an organization continues to grow, the task of tracking software assets and licenses becomes increasingly difficult to manage. Software is in a constant state of change, and organizations can easily lose track of what software is installed, where, and what licenses are in use. This dashboard focuses on the NIST CSF (CSF) ID.AM-2 subcategory, which assists in identifying and tracking multiple types of software installations and changes.
Along with hardware assets, managing software assets are just as vital in maintaining stability and security of an organization’s network. This dashboard will allow the analyst to easily identify software titles, operating systems, versions, and the number of software installations. Additionally, a list of licensed software applications and a breakdown of operating systems are included, allowing the analyst to reconcile software licenses against installations.
Another important aspect of software asset management is the detection of unsupported and outdated software and operating systems. This dashboard aids in the detection of unsupported software applications and operating systems. Any outdated software that is removed or upgraded will reduce security risks from software vulnerabilities. Additionally, the analyst will be able to easily identify unauthorized software that is present on the network. Organizations can also find this data valuable in determining end-of-life for an outdated operating system, and can assist with determine necessary costs for upgrades.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.2.0
- Nessus 8.5.1
- NNM 5.9.0
Tenable Security Center is the market-defining continuous network monitoring platform. Security Center includes active vulnerability detection with Nessus and passive vulnerability detection with Tenable’s Nessus Network Monitor (NNM). Using Security Center, the organization will obtain the most comprehensive and integrated view of its software assets.
The following components are included in this dashboard:
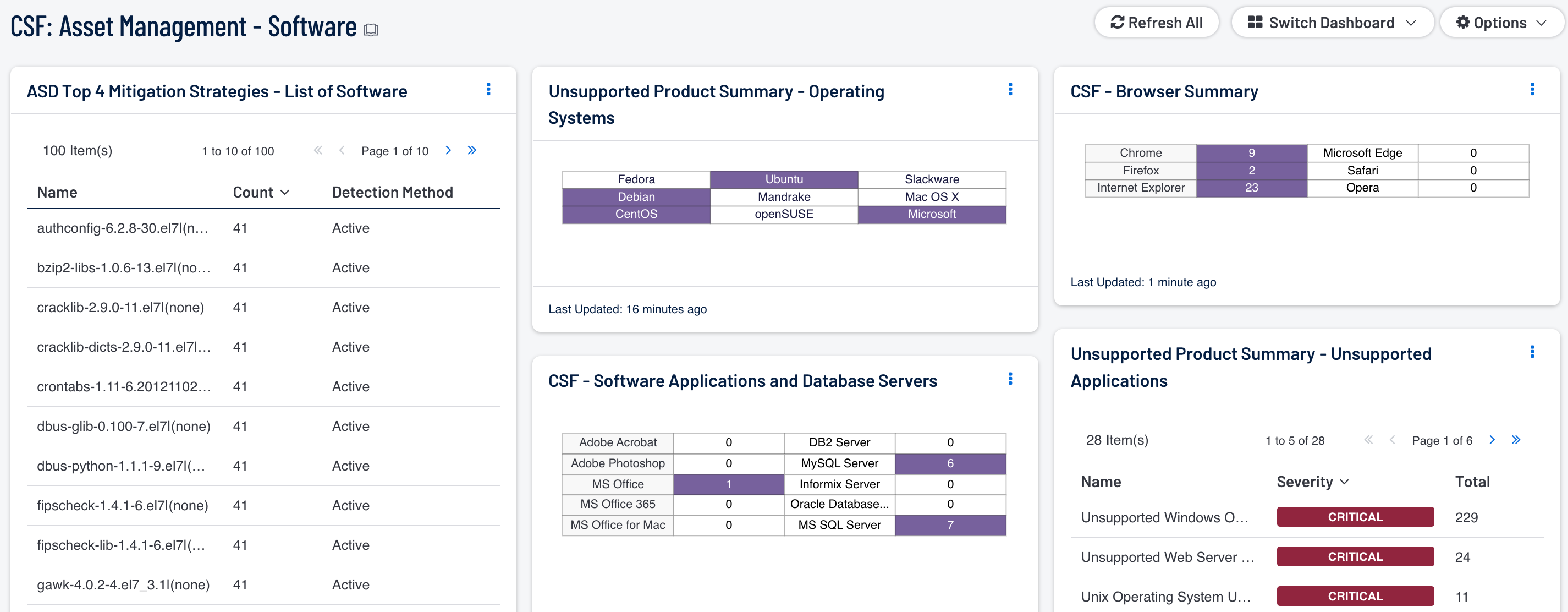
- ASD Top 4 Mitigation Strategies - List of Software: The foundation of application whitelisting is knowing what applications are installed within an organization. Security Center can collect information about installed applications using the List of Software tool, and by collecting logs from several sources such as workstations, servers, and enterprise whitelist applications. This component provides a detailed list of software currently discovered on the network. The best practice with this component is to create several copies of the component, and apply an asset or subnet to each component. Modifying the filters in this manner will provide the organization with the details for installed software for each targeted segment of the network.
- CSF - Software Applications and Database Servers: This component displays a matrix of detected software programs and database servers that are commonly used within organizations. Each matrix utilizes a combination of plugins and CPEs to detect specific software installations. If a software application or database server is detected on the network, the indicator will be highlighted in purple along with the total number of installations by count. This component can assist the organization in tracking software licenses, compliance and inventory purposes. Although the range of software applications and database servers can vary among organizations, this matrix can be modified to fit business requirements.
- Unsupported Product Summary - Operating Systems: This indicator matrix reports on operating systems that are no longer supported. The matrix displays popular operating systems, but is easily modified to fit organizational requirements. Plugin ID 33850, with vulnerability text filters that filter for the appropriate operating system name in the plugin output, alert on Unix-based operating systems that are no longer supported. Keyword filters, along with a CPE string for Microsoft, is used to alert on end-of-life Microsoft operating systems by turning the indicator purple when an alert is present.
- Unsupported Product Summary - Applications: The Unsupported Applications component displays a table of all unsupported applications by name, and sorted by severity. Displayed is the plugin ID, application name, plugin family, severity, and the total found. This component identifies unsupported applications by the “unsupported” filter against the plugin name. The table also filters on severity, dropping any informational results, and presents them via the Vulnerability Summary tool.
- CSF - Browser Summary: This matrix detects installations for the top six browsers commonly used within organizations. Many organizations have multiple browsers installed on workstations and servers. Having multiple browsers installed on systems can also increase security risk for an organization. The analyst can utilize this component in identifying systems with unapproved browsers. Additionally, this matrix can assist with patching efforts. The analyst can click on the respective browser and drill down to find additional information.