by Josef Weiss
May 18, 2016
Databases can potentially store valuable data for an organization that may not have daily database activity monitoring mechanisms in place. Many organizations involved in retail, financial, healthcare, and other industries benefit from the utilization of databases to store customer, financial, or healthcare information. Regulations such as PCI, SOX, and HIPAA have stringent compliancy requirements to safeguard this personal information of customers.
With the increased use and prevalence of databases, database management system attacks have also increased. Because of the wealth of information that is available, databases typically have a high rate of breaches among all business assets. Many times attackers take advantage of exploits or previously known vulnerabilities to gain access. Breaches and loss of data can be costly, both financially and in terms of reputation for an organization.
The Database Detection and Analysis dashboard contains components to assist in the identification of database management systems and associated vulnerabilities. Analysts are provided with vulnerability data within this dashboard, which can be easily used to assist in reducing database vulnerabilities. Components assist analysts by identifying database management systems, database events, and providing database management system specific vulnerability summaries. Active, passive, and event-based detections are utilized.
Active scanning examines the devices on the network, running processes and services, configuration settings, and vulnerabilities. Continuously monitoring the network, servers, desktops, and applications helps prioritize security efforts to mitigate threats and weaknesses. With increasing mobile and transient network devices, Tenable's Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) continuously monitors traffic, devices, applications, and communications across environments. Knowing when hosts come online and taking a zero-touch approach to assess them, the Tenable Nessus Network Monitor enables powerful, yet non-disruptive, continuous monitoring of your network. The Tenable Log Correlation Engine (LCE) enables hosts to play a part in their own security hygiene, reporting on changes in their state and security posture. This is important, because most organizations can only run scans periodically.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Monitoring.
The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.0.0
- Nessus 8.6.0
- NNM 5.9.0
- LCE 6.0.0
Tenable.sc CV provides continuous network monitoring, vulnerability identification, risk reduction, and compliance monitoring. Tenable.sc CV is continuously updated with information about advanced threats, zero-day vulnerabilities, and new types of regulatory compliance configuration audits. Tenable.sc CV allows for the most comprehensive and integrated view of network health.
The dashboard contains the following components:
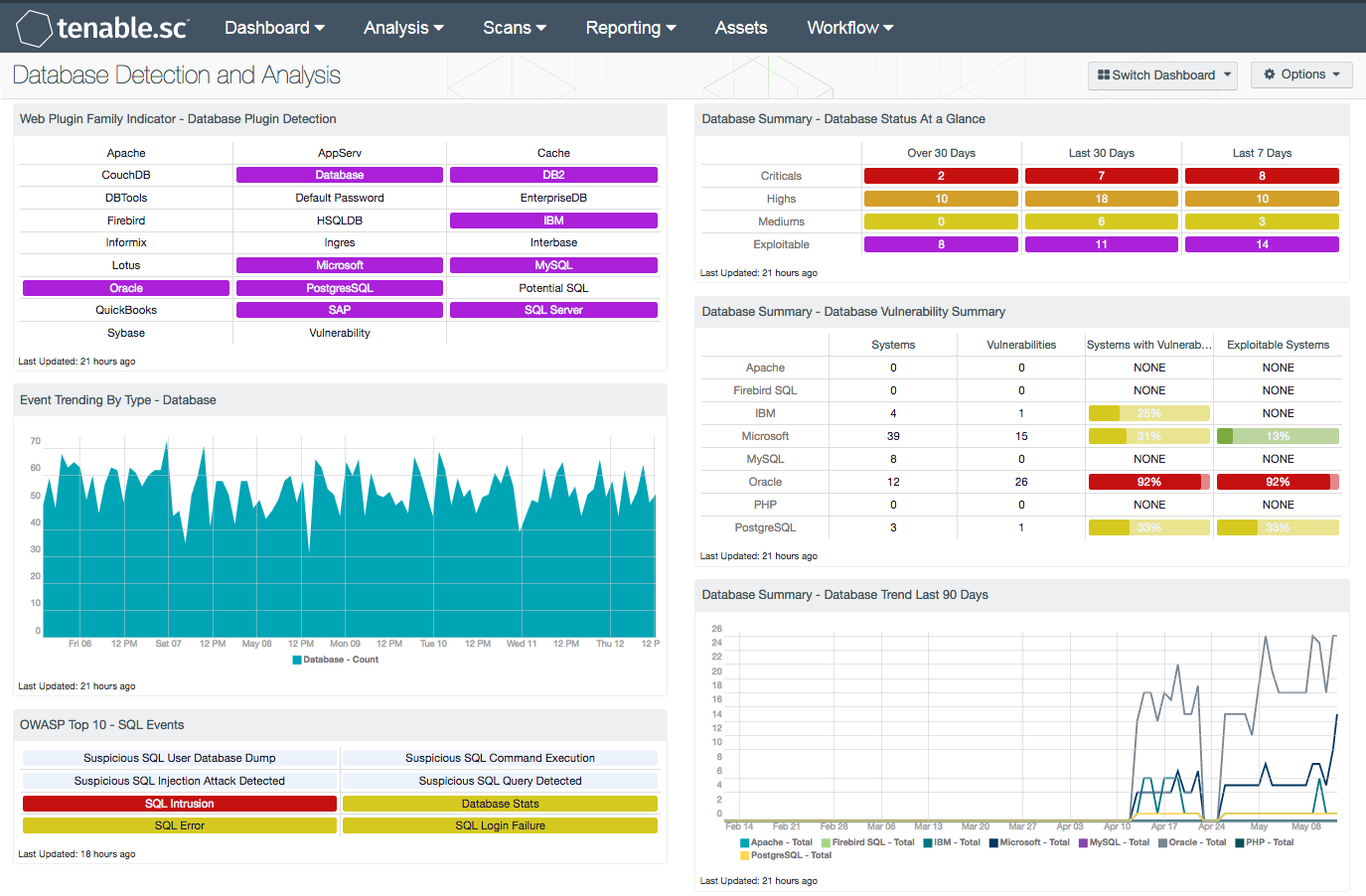
- Web Plugin Family Indicator – Database Plugin Detection: Database services in an organization are commonly set up for a very specific purpose. Analysts should be aware of database services that may be operating in the organization. This component contains indicators that turn purple when the particular database service is detected in the organization. This component lists software from major vendors, free services, and more in this component.
- Event Trending By Type – Database: This component displays a 7-day trend for logs generated by the NNM from observed SQL queries. As the NNM monitors Oracle, MySQL, and MS SQL network transactions, NNM creates logs that indicate a variety of database actions such as insertions and select statements.
- OWASP Top 10 – SQL Events: This component provides indicators for logs collected by LCE that reflect potential vulnerabilities to databases used in web applications.
- Database Summary – Database Status At a Glance: This component gives a quick visual status report on patching efforts. The number of critical, high, and medium vulnerabilities is displayed across three columns, as well as the number of days they have been detected. Represented are known vulnerabilities that have existed for Over 30 Days, the Last 30 Days, or the Last 7 Days.
- Database Summary – Database Vulnerability Summary: This component displays various defined technologies by row, and enumerates any found vulnerabilities across the columns. Presented is the number of systems on which the technology has been located, the number of identified vulnerabilities, the ratio of vulnerable systems, and the count of how many are exploitable.
- Database Summary – Database Trend Last 90 Days: This component tracks a trend of the number of vulnerabilities by installed application over the last 90 days.