by Stephanie Dunn
June 2, 2016
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is one of the most common methods used today to transfer files between clients and servers. FTP is often used within custom web applications and legacy software. Unfortunately, FTP has also become highly targeted due to the lack of secure authentication, no encryption, and the fact that FTP allows for anonymous connectivity. This dashboard will provide organizations with a comprehensive look at FTP related events, port usage, vulnerabilities, and suspicious FTP activity across the network.
FTP was originally designed as a command-line tool to transfer files across the Internet. The protocol was created in 1971 before most modern graphical user interface (GUI) based operating systems such as Windows or Mac OS X. FTP utilizes two connection modes, an active data mode and a passive command mode. In active mode, the FTP server establishes a data channel from the data port 20 on the FTP server to the FTP client port. The FTP client sends a PORT command to notify the server of client listening ports. These are high numbered ports above port 1024, and are usually blocked by most local firewalls, routers, and other security devices. Passive mode establishes connections only from the FTP client to the server on port 21. This mode requires less configuration changes, and doesn’t require new inbound connections to be made from the FTP client to the server. For passive mode, the FTP client sends a PASV command to the FTP server, and then receives the IP address and port number of the server to establish the connection.
Some organizations today still utilize FTP client software to transfer files internally, or have incorporated FTP into custom web applications or legacy software that house confidential corporate data. FTP by design is an insecure protocol that transmits data in clear text and has no ability to encrypt traffic. This feature makes it easy for anyone to sniff FTP traffic and easily gain access to FTP account credentials. Using FTP in any capacity can present significant security risks for an organization. Organizations should look to transition to more secure transfer protocols such as SSH, which provides a secure channel for transmitting files across the Internet. To provide an additional layer of protection, organizations should also encrypt files stored on FTP servers, which will help to ensure data confidentially and integrity.
This dashboard can provide security teams with valuable information on FTP network traffic, which can assist in detecting suspicious FTP activity, data leakage, and unauthorized FTP software installed on the network. Components within this dashboard can alert analysts to FTP servers using custom ports or other services using the default FTP server port 21. Security teams can use the information presented within this dashboard to detect and disable systems using anonymous FTP. Having anonymous access enabled allows anyone to access an FTP server without credentials, and can present serious security risks for an organization. Many organizations today access custom or legacy applications that utilize or require FTP access for business purposes. By continuously monitoring both FTP client and server activity, organizations can help to ensure that confidential data is being transferred in a secure manner.
This dashboard is available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, Assurance Report Cards, and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Discovery & Detection. The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.3.2
- Nessus 8.6.0
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
- Compliance Data
Only Tenable can automatically analyze information from active scanning, intelligent connectors, agent scanning, passive listening, and host data. Active scanning periodically examines hosts to determine the level of risk posed to the organization. Intelligent connectors leverage other security investments in the environment to integrate security data in order to improve context and analysis. Agent scanning enables organizations to rapidly assess hosts without the need for credentials. Passive listening detects hosts that were offline during active scans, and provides real-time monitoring to collect information about each host and how the hosts are communicating on the network. Host data is analyzed and monitored to correlate real-time events and identify malicious activity and anomalous behavior from users, operating systems, network devices, and other critical infrastructure. Each sensor delivers continuous visibility and critical context, enabling decisive action that transforms a security program from reactive to proactive.
The following components are included in this dashboard:
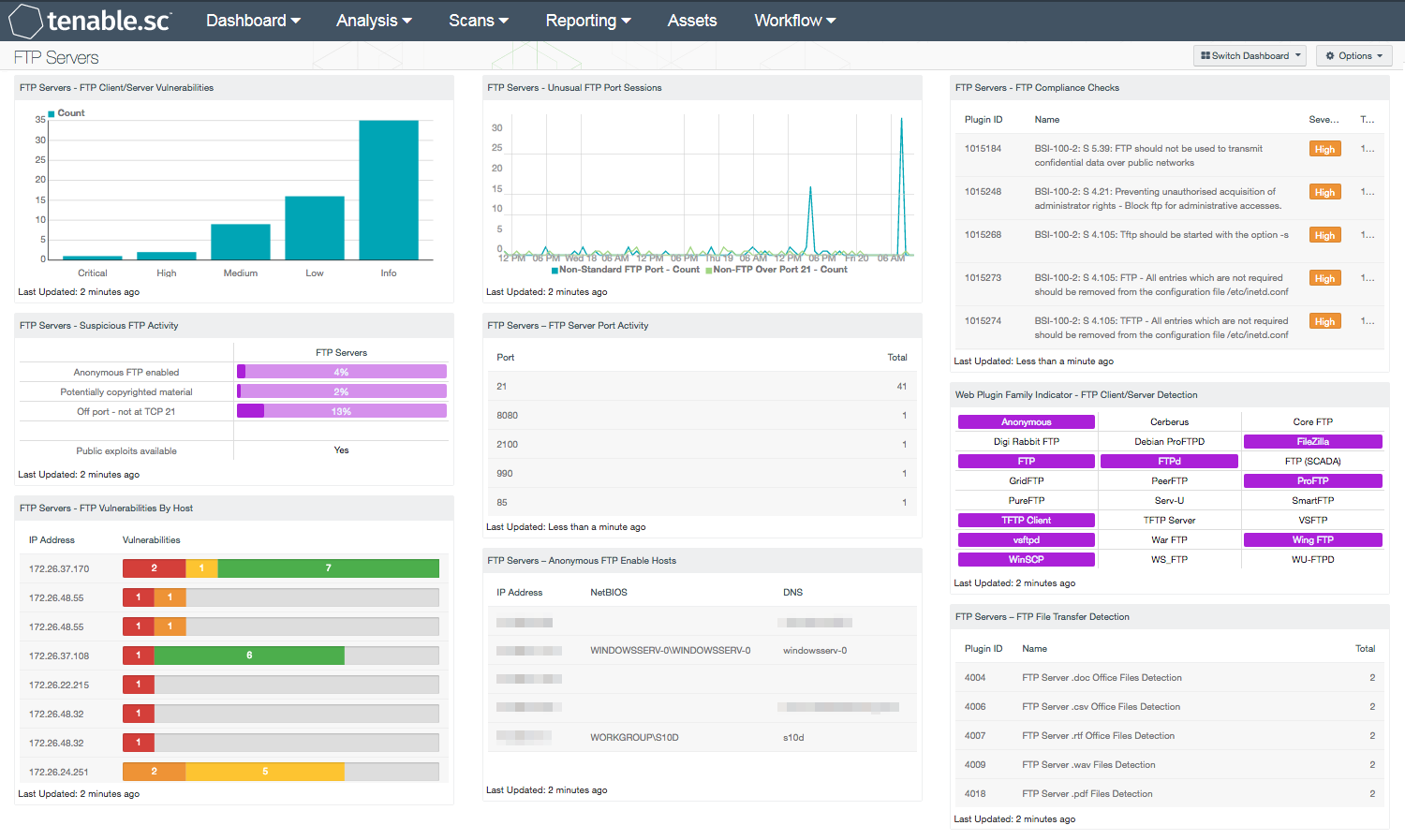
- FTP Servers – FTP Client/Server Vulnerabilities: The FTP Client/Server Vulnerabilities chart provides an overview of FTP client and server vulnerabilities. This chart detects FTP plugins using active scanning and passive listening to identify FTP traffic during and in between scans. Analysts can use the information presented within this chart to detect and remediate FTP related vulnerabilities. This chart can be modified based on organizational needs.
- FTP Servers - Suspicious FTP Activity: The Suspicious FTP Activity matrix component highlights the percentage of FTP servers that have anonymous FTP login enabled, contain potentially copyrighted material, and run on ports other than port 21. The component also includes publicly exploitable FTP related vulnerabilities. Additional rows can be added to highlight FTP service characteristics and properties that are of interest.
- FTP Servers - FTP Vulnerabilities By Host: The FTP Vulnerabilities By Host table presents a list of hosts with FTP related vulnerabilities. Information within this table includes Critical, High, Medium, and Low severity level vulnerabilities, and is sorted by score. The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) is an open industry standard for assessing the severity of vulnerabilities. CVSS scores are assigned to vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to prioritize resources according to the score. The scores range from 0 to 10. Vulnerabilities with a base score in the range 7.0-10.0 are critical, those in the range 4.0-6.9 are major, and those in the range 0.0-3.9 are minor. The CVSS scores correspond to the Tenable severity levels as follows: 10.0 = Critical severity, 7.0-9.9 = High, 4.0-6.9 = Medium, and 0.0-3.9 = Low. This information can help organizations to assess and prioritize current risks.
- FTP Servers - Unusual FTP Port Sessions: The Unusual FTP Port Sessions chart presents a 72-hour trend of non-standard FTP port activity and non-FTP activity over port 21 on the network. Activity from non-standard FTP ports relies upon NNM detections that alert when hosts are running non-FTP traffic over port 21. This type of traffic may indicate FTP activity using custom ports. Non-FTP traffic over port 21 may indicate applications using port 21 to communicate across the network. Many applications can be configured to use a default or customized port number. Organizations should note any web applications, FTP servers, or services utilizing custom ports.
- FTP Servers – FTP Server Port Activity: The FTP Server Port Activity table presents a port summary of FTP Server activity. Using the Nessus plugin 10092, organizations will be able to detect FTP servers utilizing custom ports, along with active and passive FTP connections. In active mode, the FTP server establishes a data channel from the data port 20 on the FTP Server to the FTP client port. The FTP client sends a PORT command to notify the server of client listening ports. These are high numbered ports above port 1024, and are usually blocked by most local firewalls, routers, and other security devices. Passive mode establishes connections only from the FTP client to the server on port 21. This mode requires less configuration changes, and doesn’t require new inbound connections to be made from the FTP client to the server. For passive mode, the FTP client sends a PASV command to the FTP server, and then receives the IP address and port number of the server to establish the connection. Analysts can use the information presented within this table to monitor FTP activity and detect custom FTP ports in use.
- FTP Servers - Anonymous FTP Enabled Hosts: The Anonymous FTP Enabled Hosts table reports on systems that have anonymous FTP logins enabled. Having anonymous access enabled allows anyone to access an FTP server without credentials, and can present serious security risks for an organization. Security teams can use the information presented within this table to detect and disable systems using anonymous FTP. Analysts and security teams should continuously monitor FTP servers to ensure that sensitive content is not being transferred in clear text.
- FTP Servers - FTP Compliance Checks: The FTP Compliance Checks component provides a summary of FTP related compliance checks. Many organizations are required to follow compliance regulations, such as PCI DSS, which require monitoring and configuring FTP securely as a part of compliance objectives. This table uses the FTP, FTP Client, and FTP Server plugin families and the “Compliance” plugin type to highlight FTP compliance check results. High severity denotes checks that have failed to meet the compliance threshold. Medium severity shows checks that need to be manually reviewed to assess their compliance state. Organizations should review current security policies and compliance requirements that are relevant to the organization. Each compliance check includes detailed information on the respective vulnerability that the analyst can immediately drill down into. The analyst can drill down to obtain IP addresses, possible solutions, and additional information to aid with compliance.
- Web Plugin Family Indicator - FTP Client/Server Detection: The FTP Client/Server Detection matrix present indicators that alert when FTP clients and servers have been detected on the network. FTP services in an organization are commonly set up for a very specific purpose. Analysts should be aware of FTP services that may be operating in the organization, as well as the type of FTP services. This component contains indicators that turn purple when the particular FTP client or server is detected on the network.
- FTP Servers - FTP File Transfer Detection: The FTP File Transfer Detection table reports on systems hosting files on an FTP server. This component detects commonly used file formats and applications such as PDF, ZIP, RTF, and Microsoft Office based files. Organizations can use the information within this table to ensure that hosted files do not contain confidential data. This table can be modified to include specific or additional information per organizational requirements.