by Cesar Navas
November 19, 2020
The National Information Assurance (NIA) Policy v2.0 specifies that an effective security program requires the active engagement of executive management to address emerging threats and provide strong cyber security leadership. The term used to describe executive management’s engagement is, Information Security Governance.
NIA v2.0 Information Security Governance requires that agencies include security in the development of software and acquisition. Tenable recommends using the Cyber Exposure Lifecycle model in conjunction with NIAv2 compliance efforts. The Lifecycle is composed of three main parts, see, predict, and act. The first stage, see, includes identifying and mapping assets across any computing environment. Tenable.sc provides multiple methods of detecting software and accounts including active and passive scanning. The NIA Secure Software Summary dashboard can assist the organization by identifying vulnerabilities and events associated with weak programming practices.
Applying secure coding practices, code reviews, regular vulnerability scans and penetration tests help to reduce risk related to software development. In addition to tracking source code changes, software libraries and supporting applications can easily be over looked. Software managers and risk managers are able to use this dashboard to work in unison to identify risks. When development is outsourced, independent vulnerability scanning of the applications will help identify any potential security risks.
The NIA Secure Software [SS] domain contains technical controls related to ensuring that security is involved in the Software Development Life Cycle [SDLC]. These controls include removing and disabling software or undesired functionality. Ensuring patching is up-to-date is important to secure potentially vulnerable software. Security and development teams can use this dashboard to help stop attacks before they begin. The OWASP Top 10 web security flaws will detect threats such as:
- Local File Inclusion (LFI)
- Remote File Inclusion (RFI)
- Directory Traversal, cross-site scripting (XSS), and
- Web server vulnerabilities.
Tenable.sc detects injection activity; session attacks, repeated password guessing, and unauthorized privilege attempts. Both Nessus and Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) detect specific vulnerabilities from development kits, frameworks, libraries, common IDEs, and development software. This dashboard assists organizations in strengthening application development by quickly identifying security flaws that impact critical systems.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Tenable.sc Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Tenable.sc Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Tenable.sc 5.14.1
- Nessus 8.11.1
- Compliance data
Tenable.sc Continuous View (CV) is the market-defining On-Prem Cyber Exposure Platform. Tenable.sc CV provide the ability to continuously Assess an organization’s adherence to best practice configuration baselines. Tenable.sc provides customers with a full and complete Cyber Exposure platform for completing an effective Information Security Management System program prescribed by the NIA standard.
Components
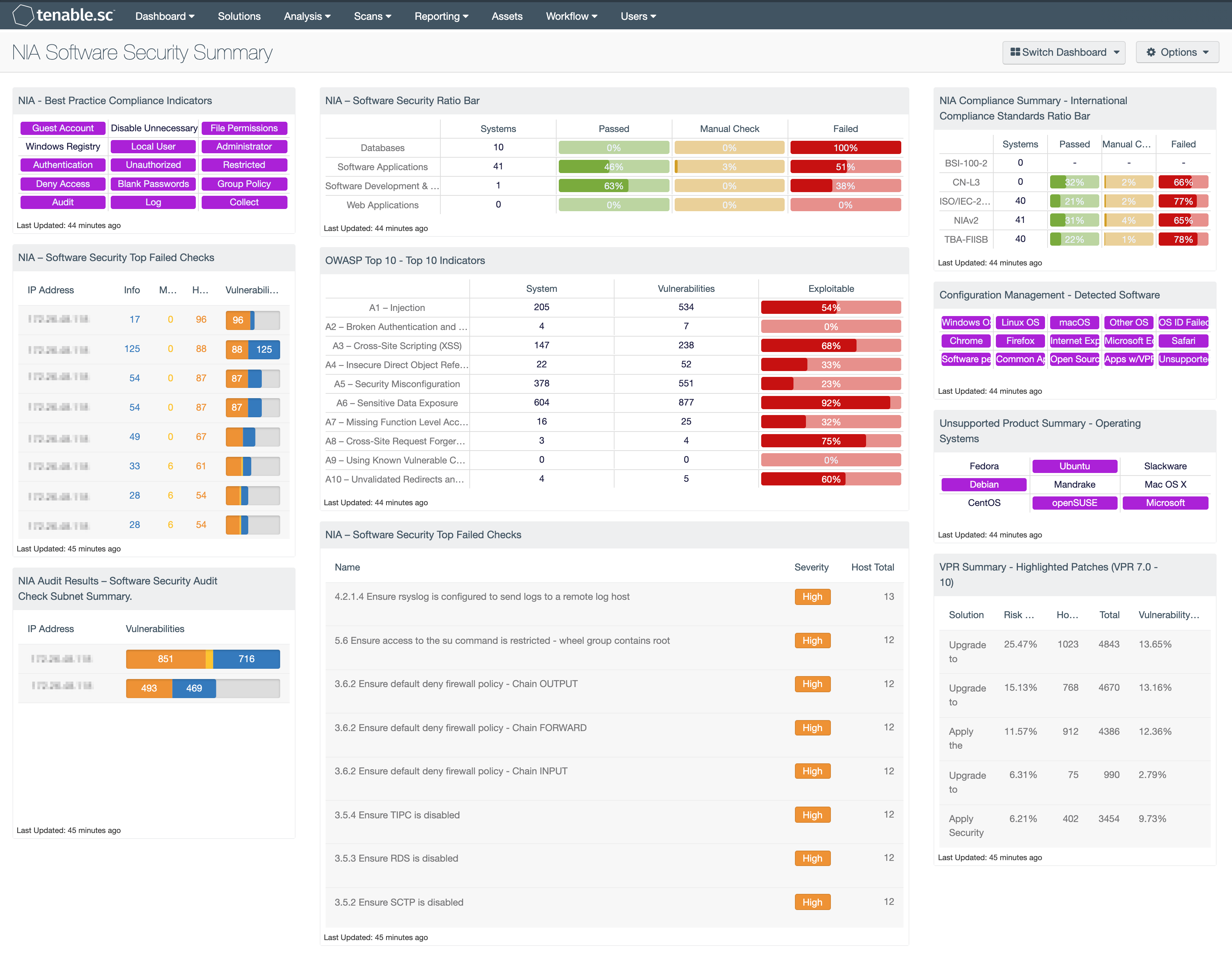
NIA – Software Security Ratio Bar: This matrix displays a summary of several key targets in the Software Security domain, providing hosts count and ratio bars for each severity level.
NIA – Software Security Top Failed Checks: The NIA – Software Security Top Failed Checks table provides a list of the top 100 systems on the network with NIA Software Security compliance audits.
NIA Audit Results – Software Security Audit Check Subnet Summary: The NIA Audit Results – Software Security Audit Check Subnet Summary table provides a summary of NIA audit results for the top 30 affected subnets related to the Software Security domain.
NIA - Best Practice Compliance Indicators: This component uses results from the NIA compliance audit to trigger on specific plugin keywords for best practice configuration guidelines. When the keyword or phrase has been detected within the plugin name, the indicator will turn purple. The analyst can click on the indicator and drill down to obtain additional information on hosts affected. This matrix will allow the analyst to readily identify specific compliance best practice keywords, and can be modified to suit organizational needs.
OWASP Top 10 - Top 10 Indicators: This component collects the vulnerabilities from the CGI Abuses, CGI Abuses : XSS, and Web Servers plugin families for both active and passive vulnerabilities. The CGI Abuses family Checks for web-based CGI programs with publicly documented vulnerabilities. These checks include SQL injection, Local File Inclusion (LFI), Remote File Inclusion (RFI), Directory Traversal, and more. For web-based CGI programs with publicly documented cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, the CGI Abuses : XSS plugin family is used. For web server vulnerabilities, the Web Server plugin family can detect vulnerabilities in web servers such as Apache HTTP Server, IBM Lotus Domino, Microsoft IIS, and many more.
Compliance Summary - International Compliance Standards Ratio Bar: This matrix displays a summary of several cross-referenced standards that are based on well-known international controls, providing hosts count and ratio bars for each severity level. The three columns with ratio bars show the ratio of total audit checks to a specified status of the check. Checks that have passed are green, failed checks are red, and checks that require manual verification are orange.
Configuration Management - Detected Software: This matrix presents indicators for operating systems, browsers, unsupported, and other software installations on systems within a network. Indicators will turn purple when a match is found and will display a list of detected software. Analysts will find this information useful in tracking software licenses, and identify hosts running unauthorized or malicious software. Additionally, the data provided within this component can be used to monitor systems running unsupported software, which can contain vulnerabilities and place critical systems at risk. Filters within this component can be modified to include additional or specific software per organizational requirements.
Unsupported Product Summary - Operating Systems: This indicator matrix reports on operating systems that are no longer supported. The matrix displays popular operating systems but is easily modified to fit organizational requirements. Plugin ID #33850, with vulnerability text filters that filter for the appropriate operating system name in the plugin output, alert on Unix-based operating systems that are no longer supported. Keyword filters, along with a CPE string for Microsoft, is used to alert on end-of-life Microsoft operating systems by turning the indicator purple when a vulnerable asset is present.