by Cody Dumont
February 3, 2015
Shell related threats, such as the recently released Shellshock vulnerability, are on the rise. Detecting unauthorized shell access can become a full-time job. Customers with Security Center can use this dashboard to easily identify shell related vulnerabilities. The systems and vulnerabilities identified in this dashboard allow system admins to quickly identify the threats related to shell access and quickly identify the source of the notification. This dashboard contains components that utilize active, passive, compliance, and event vulnerability detection. Additionally, there are two components that assist with log analysis.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Threat Detection & Vulnerability Assessments.
The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 4.8.2
- Nessus 8.6.0
- LCE 6.0.0
- NNM 5.9.0
By understanding the detection method, system administrators can better determine if a shell session has been exploited or is a potential method of exploitation. For example, there are several passive detections of “Shell Attacks” and “Generic Shell” detection. When these plugins are triggered, an attacker is actively exploiting the system. When the active or compliance vulnerabilities are detected, the system is at risk of being exploited. The event types are logs, which may indicate an exploit in the past.
Several of the indicator components provide saved queries of both vulnerability data and log data collected by the Log Correlation Engine (LCE). These searches aid analysts in detecting vulnerabilities related to shell access, backdoor, and botnet activities. The “Shellshock” indicator uses several CVEs to quickly identify vulnerable systems. The vulnerability indicators use a keyword search combined with plugin type to identify vulnerable systems, while the event indicators use a keyword combined with event type to identify logs that should be reviewed.
Tenable provides continuous network monitoring to identify vulnerabilities, reduce risk, and ensure compliance. Security Center includes Nessus for active detection and Nessus Network Monitor (NNM) for passive vulnerability detection. Security Center proactive continuous monitoring identifies an organizations biggest risk across the entire enterprise. Nessus is continuously updated with information about advanced threats and zero-day vulnerabilities to allow for continuous identification of shell based vulnerabilities. NNM conducts deep packet inspection enabling discovery and assessment of operating systems, network devices, and other critical infrastructure devices.
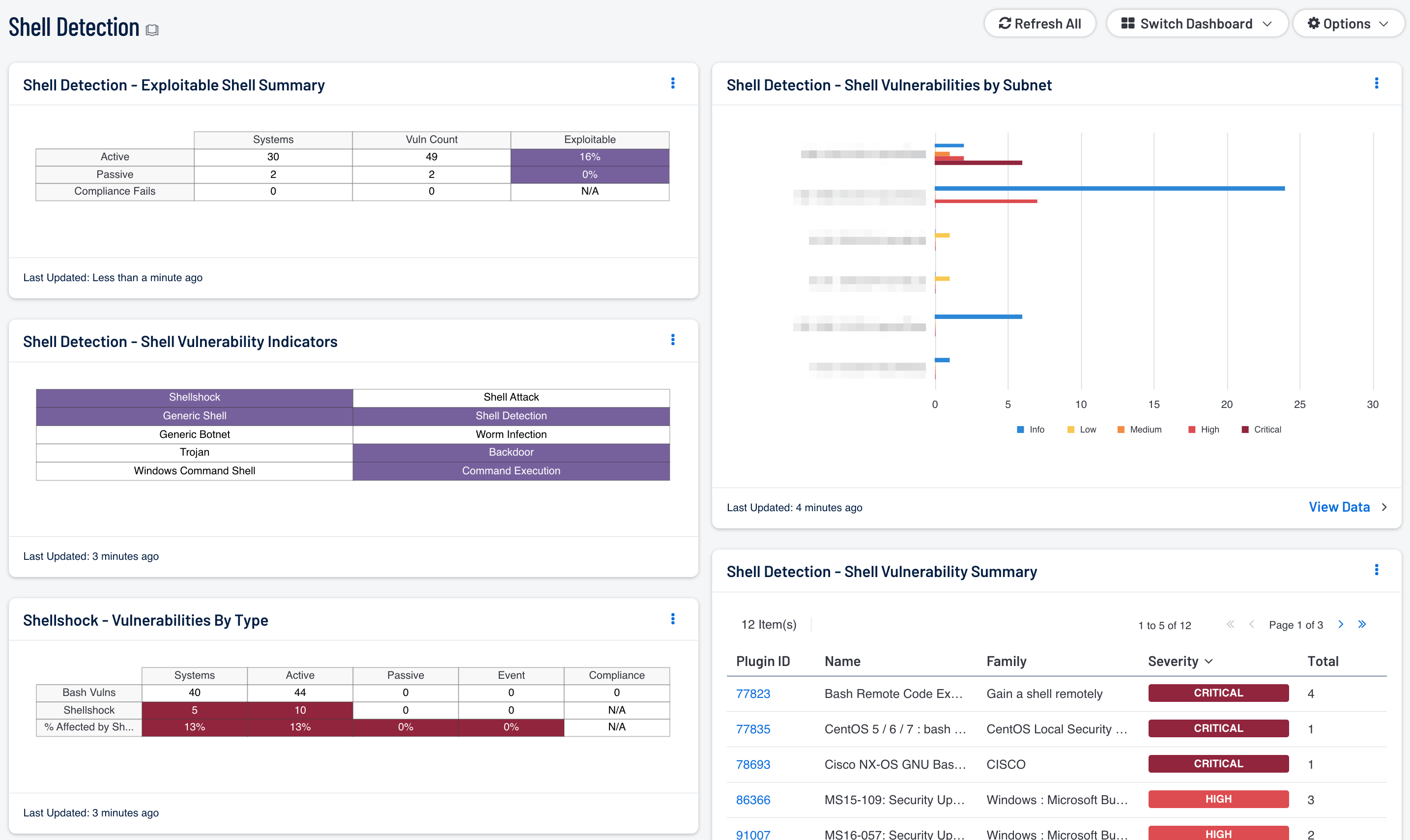
Shell Detection - Exploitable Shell Summary: The systems and vulnerabilities identified in this component allow the system admin to quickly identify if a threat related to shell access is based on active, passive, compliance, or event vulnerabilities. By understanding the detection method, system administrators can better determine if a shell session has been exploited or is potential method of exploitation. For example, there are several passive detections of “Shell Attacks” and “Generic Shell” detection When these plugins are triggered, an attacker is actively exploiting the system. When the active or compliance vulnerabilities are detected, the system is at risk of being exploited. The event types are logs, which may indicate an exploit in the past.
Shell Detection - Shell Vulnerability Indicators: Shell Vulnerability Indicators provides indicators for the most effective shell-related search within the vulnerability data. This aids in the detection of vulnerabilities related to shell access, backdoor, and botnet activities.
Shellshock - Vulnerabilities By Type: This component displays information about systems on the network with vulnerabilities related to bash. The first row contains detected general bash vulnerabilities, the second row contains detected Shellshock specific vulnerabilities, and the third row calculates the percentage of the general bash vulnerabilities that are Shellshock vulnerabilities.
Shell Detection - Shell Vulnerabilities by Subnet: This chart provides a shell vulnerability summary by subnet. When analyzing risk in an organization, the security team needs to understand where the highest risks are detected. This component provides a view into the top 10 networks with a summary bar for each severity, informational through critical.
Shell Detection - Shell Vulnerability Summary: This table provides a list of shell vulnerabilities sorted by severity. This view provides a quick overview of the current shell vulnerabilities on the network. The analyst will need to drill down into each vulnerability to fully understand the associated risk.