CVE-2020-5902: Critical Vulnerability in F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI) Actively Exploited

Three days after an advisory was disclosed for a critical remote code execution vulnerability in F5’s BIG-IP, active attempts to exploit vulnerable hosts have been observed in the wild.
Update July 8, 2020: F5 has provided updated mitigation details after reports that researchers had discovered a way to bypass some of the mitigations. The Solutions section of our blog has been updated accordingly.
Background
On June 30, F5 Networks published support articles identified as K52145254 and K43638305 to address two vulnerabilities in BIG-IP, its family of products which includes software and hardware solutions that provide access control, application availability and security solutions. These products include:
- Local Traffic Manager (LTM)
- Application Acceleration Manager (AAM)
- Advanced Firewall Manager (AFM)
- Analytics
- Access Policy Manager (APM)
- Application Security Manager (ASM)
- Domain Name System (DNS)
- Fraud Protection Service (FPS)
- Global Traffic Manager (GTM)
- Link Controller
- Policy Enforcement Manager (PEM)
The vulnerabilities were disclosed to F5 by Mikhail Klyuchnikov, a senior web application security researcher at Positive Technologies.
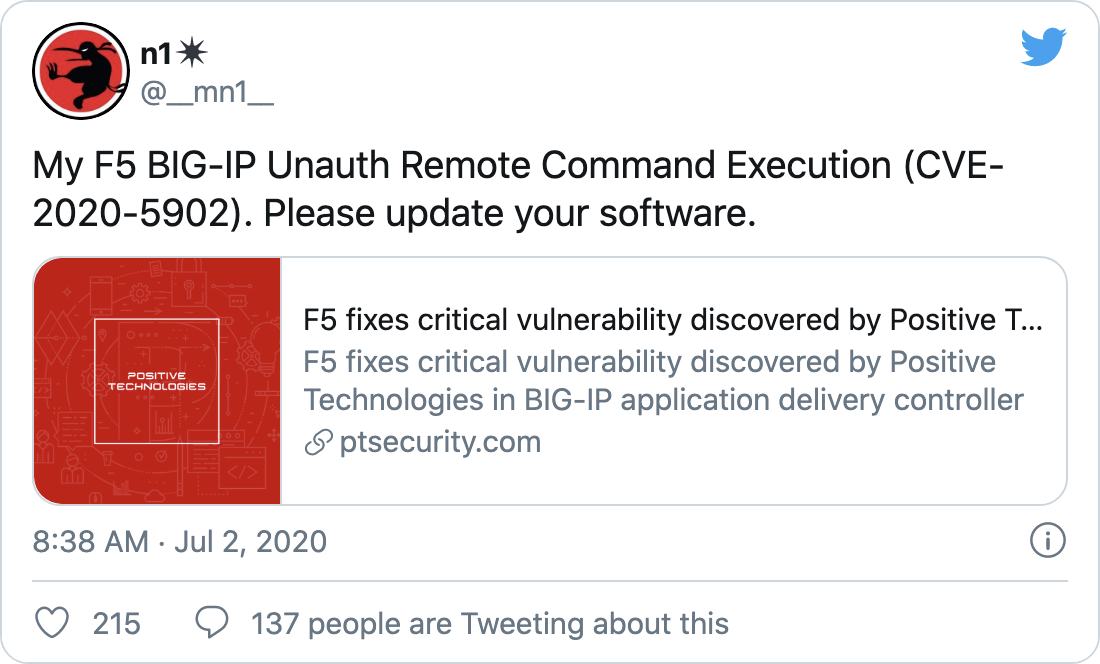
Analysis
CVE-2020-5902 is a critical vulnerability in the BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface (TMUI) also known as the Configuration Utility. The vulnerability received a CVSSv3 rating of 10.0, the highest possible score. The vulnerability is exploitable when network access to the TMUI is exposed via the BIG-IP management port or Self IPs. Successful exploitation of this flaw would grant an attacker a variety of privileges, including the ability to execute arbitrary system commands or Java code, create or delete files, as well as disable services on the vulnerable host. The advisory states that the vulnerability could also “result in complete system compromise.”
CVE-2020-5903 is a cross-site scripting vulnerability in TMUI/Configuration Utility. This vulnerability received a CVSSv3 rating of 7.5, which makes this a “high” severity flaw. According to F5’s advisory, exploitation would grant an attacker the capability to execute JavaScript code under the same privileges as the current user. If the current user has administrative privileges that grant them Advanced Shell access, an attacker would be able to “completely compromise the BIG-IP system through Remote Code Execution.”
Another path traversal flaw emerges
CVE-2020-5902 evokes comparisons to CVE-2019-19781, a remote code execution vulnerability in the Citrix Application Delivery Controller (ADC) and Gateway that was disclosed in December 2019, and for which exploit scripts quickly emerged. Both vulnerabilities are path traversal flaws in their respective products, and the Citrix vulnerability was also discovered by Klyuchnikov.
Default configuration exposure of TMUI
According to Ben Goerz, a senior manager of counter-threat management at Kimberly-Clark, the TMUI is exposed under default configurations due to the usage of Self IPs.
TMUI also runs on Self IPs by default. So a lot of orgs accidentally/lazily exposed it when setting up VLANs for their public IPs.
— Ben Goerz (@bengoerz) July 4, 2020
A senior security engineer at F5 elaborated further that BIG-IP versions 11.5.3 and later have switched the default behavior of Self IPs to “Allow None,” whereas versions 11.5.2 and prior use “Allow Default” for Self IPs. They added that when upgrading from a previous version, the existing configuration is carried over, including on devices after 11.5.3. Users will need to update this configuration after upgrading.
Correct. 11.5.3 and later releases have Allow None as default for Self-IPs. 11.5.2 and earlier have Allow Default.
— MegaZone (@megazone) July 4, 2020
Note that upgrading from earlier versions keeps the existing config. So if the config dates back to an older version this may need to be changed.
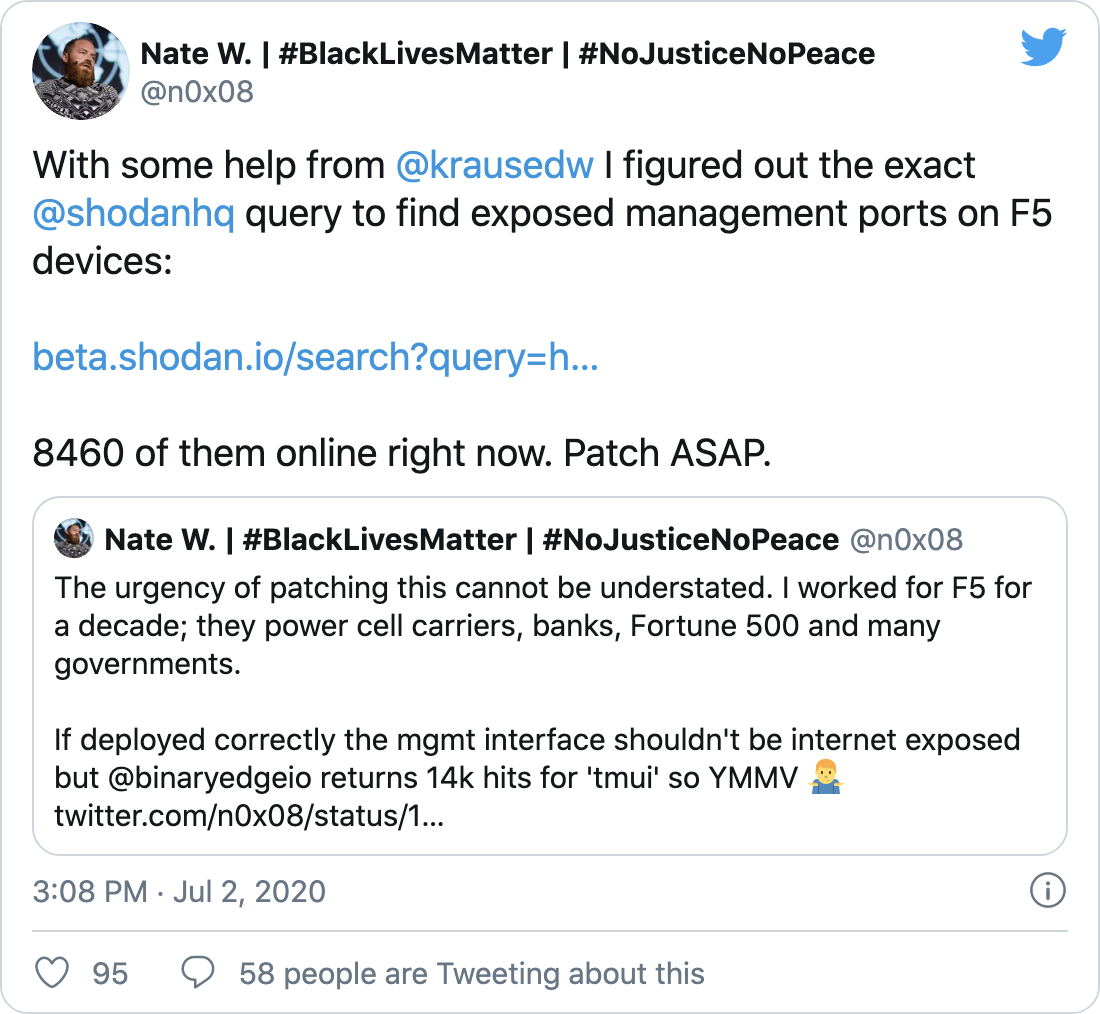
Over 8,000 accessible hosts with exposed management ports
According to Nate Warfield from Microsoft's Security Response Center, there are over 8,000 accessible hosts with exposed management ports.
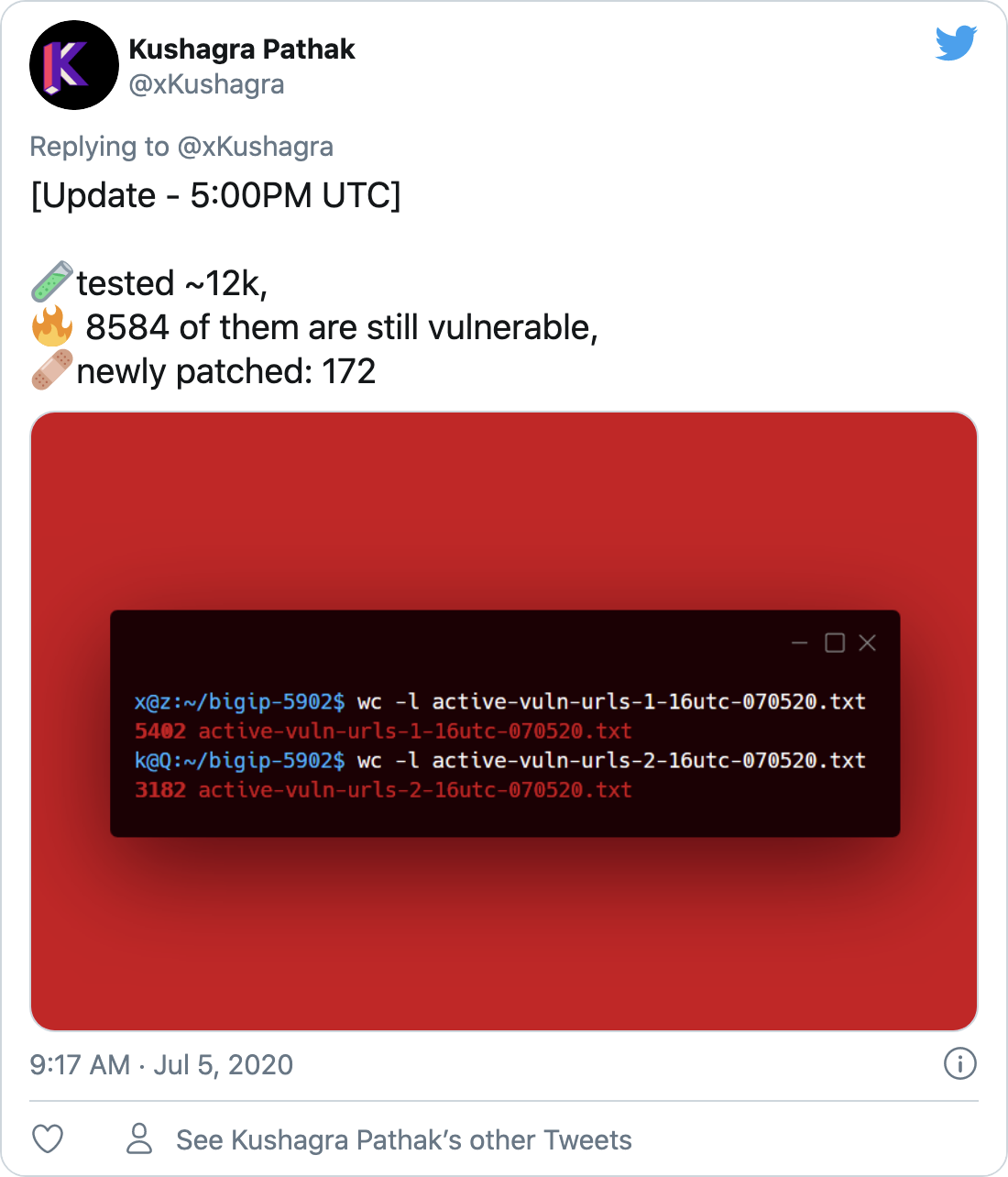
Security researcher Kushagra Pathak has scanned over 12,000 hosts and confirmed around 8,500 remain vulnerable.
Active exploitation observed in the wild
According to several reports, active scanning and exploitation of CVE-2020-5902 have already been observed. NCC Group specifically notes that attackers are leveraging the vulnerability to try to capture “web.xml” or “/etc/hosts” from vulnerable hosts.
We're seeing active exploitation of the @F5Networks K52145254: TMUI RCE vulnerability #CVE-2020-5902 issue. The threat actor is after web.xml or /etc/hosts - https://t.co/9AKpWGSrEj.
— NCC Group Infosec (@NCCGroupInfosec) July 4, 2020
Additionally, Kevin Beaumont, senior threat intelligence analyst at Microsoft, discovered that attackers had planted a cryptocurrency miner on one of his F5 honeypots.
My CVE-2020-5902 honeypot got owned to upload..
— Kevin Beaumont (@GossiTheDog) July 5, 2020
Wait for it..
A coin miner. pic.twitter.com/AxQlSVWG6Y
We anticipate exploitation attempts will increase in the coming days, now that more proof of concept (PoC) scripts have been published and researchers are sharing more details publicly.
Potential impact of CVE-2020-5902
A Twitter thread published by a security researcher known as “kevvyg” calls this vulnerability “one of the most impactful” they’ve seen in decades because of its “ability to compromise any application sitting behind one [LTM or GTM].” This comment underscores the severity of the flaw, and its CVSS score highlights just how simple it is to exploit.
This is probably one of the most impactful vulnerabilities I've seen in my 20+ years in infosec. It's not just the ability to compromise one LTM or GTM. It's the ability to compromise any application sitting behind one. (8/x)
— kevvyg and the Wrong Opinions (@kevvyg) July 5, 2020
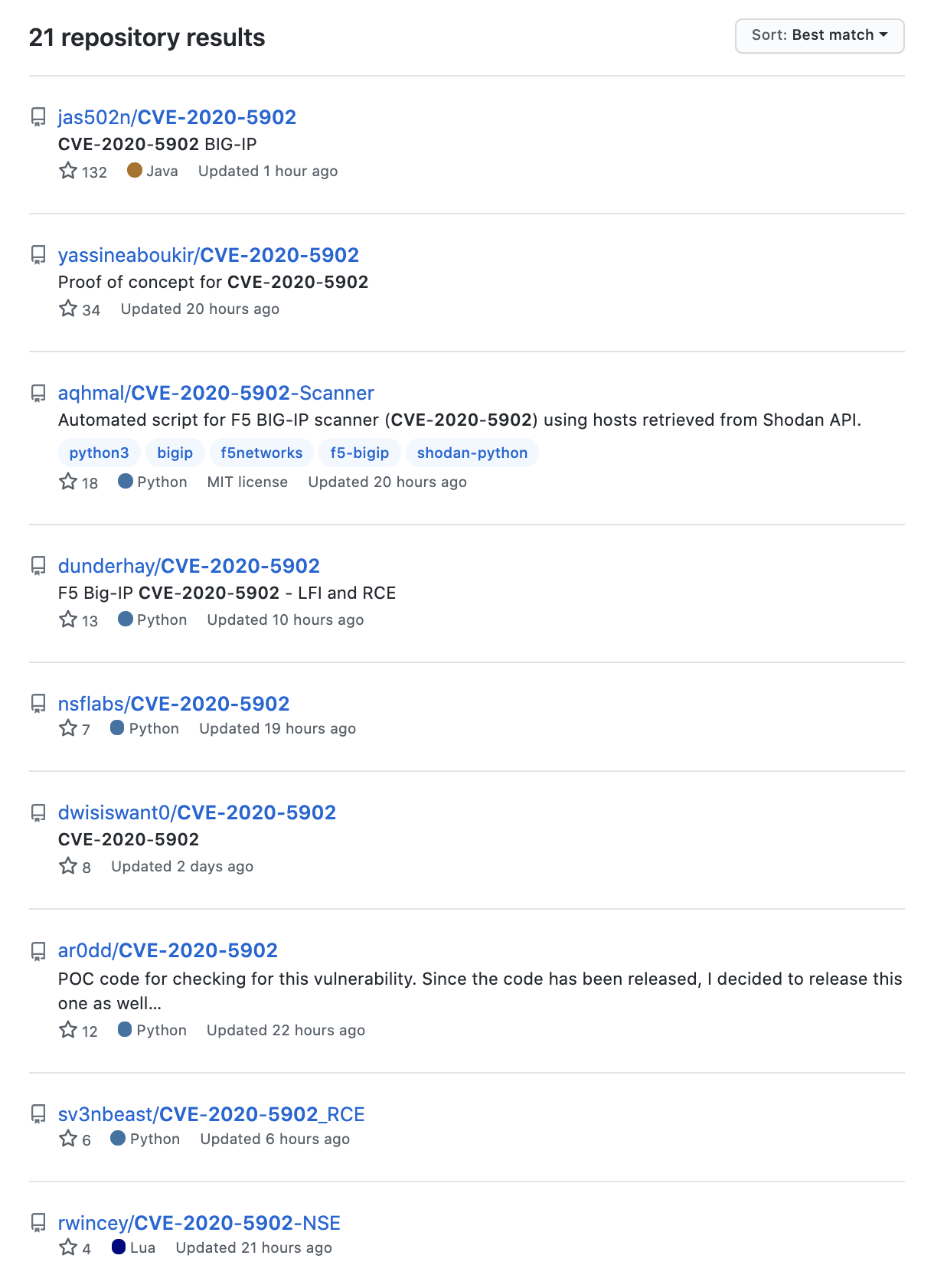
Proof of concept
Several PoC scripts for CVE-2020-5902 have been published to GitHub. However, at the time this blog was published, there was no PoC for CVE-2020-5903.
Solution
F5 has released patches to address both vulnerabilities across its suite of products. The following table lists the branch and affected versions, as well as fixed versions.
| Branch | Affected Versions | Fixed Version |
|---|---|---|
| 11.x | 11.6.1 through 11.6.5 | 11.6.5.2 |
| 12.x | 12.1.0 through 12.1.5 | 12.1.5.2 |
| 13.x | 13.1.0 through 13.1.3 | 13.1.3.4 |
| 14.x | 14.1.0 through 14.1.2 | 14.1.2.6 |
| 15.x | 15.0.0 | None |
| 15.1.0 | 15.1.0.4 |
Patching this vulnerability should be a priority, as the United States Cyber Command warned that for both flaws organizations should “remediate immediately.”
URGENT: Patching CVE-2020-5902 and 5903 should not be postponed over the weekend. Remediate immediately. https://t.co/UBKECuN7Vv
— USCYBERCOM Cybersecurity Alert (@CNMF_CyberAlert) July 3, 2020
If patching is not feasible at this time, F5 provides several temporary mitigations that are sufficient to address the vulnerability:
- F5 recommends that you should permit management access to F5 products only over a secure network. If possible, deny all public access as a best practice.
- For Self IPs, F5 recommends blocking access to TMUI via Self IPs. This is achieved by modifying the Port Lockdown setting for each Self IP by setting it to Allow None. The preferred way to open ports on the device is to use the Allow Custom setting and prevent access to the TMUI.
- For TMUI, F5 recommends restricting management access to the Configuration Utility in its products by using source IP filtering.
Despite some of these temporary mitigations, F5 warns that authenticated users capable of accessing the TMUI will “always be able to exploit this vulnerability” until the vulnerable host is patched, which is why patching is the preferred fix. As F5 has made updates to their mitigation recommendations on July 8, we recommend reviewing the advisories frequently if patching may be delayed to ensure that any further recommendations can be applied.
Identifying affected systems
A list of Tenable plugins to identify these vulnerabilities can be found here. Please note that, due to a technical issue, plugin ID 137918 was originally labeled as “Low” severity. The plugin has since been corrected to reflect the proper severity.
Get more information
- F5 Support Article for CVE-2020-5902
- F5 Support Article for CVE-2020-5903
- Positive Technologies News Alert for CVE-2020-5902 and CVE-2020-5903
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.
- Vulnerability Management

