Microsoft’s September 2024 Patch Tuesday Addresses 79 CVEs (CVE-2024-43491)

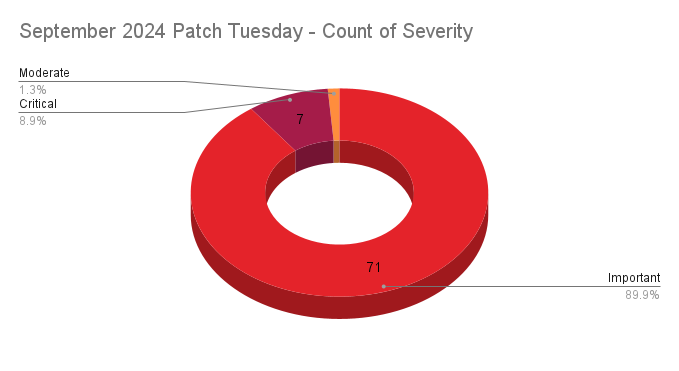
- 7Critical
- 71Important
- 1Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft addresses 79 CVEs with seven critical vulnerabilities and four zero-day vulnerabilities, including three that were exploited in the wild.
Microsoft patched 79 CVEs in its September 2024 Patch Tuesday release, with seven rated critical, 71 rated as important, and one rated as moderate.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- Azure CycleCloud
- Azure Network Watcher
- Azure Stack
- Azure Web Apps
- Dynamics Business Central
- Microsoft AutoUpdate (MAU)
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 (on-premises)
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Management Console
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office Publisher
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Office Visio
- Microsoft Outlook for iOS
- Microsoft Streaming Service
- Power Automate
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- SQL Server
- Windows Admin Center
- Windows AllJoyn API
- Windows Authentication Methods
- Windows DHCP Server
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel-Mode Drivers
- Windows Libarchive
- Windows MSHTML Platform
- Windows Mark of the Web (MOTW)
- Windows Network Address Translation (NAT)
- Windows Network Virtualization
- Windows PowerShell
- Windows Remote Access Connection Manager
- Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service
- Windows Security Zone Mapping
- Windows Setup and Deployment
- Windows Standards-Based Storage Management Service
- Windows Storage
- Windows TCP/IP
- Windows Update
- Windows Win32K - GRFX
- Windows Win32K - ICOMP

Elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 38% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities at 29.1%.
CVE-2024-43491 | Microsoft Windows Update Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-43491 is a RCE vulnerability in Microsoft Windows Update affecting Optional Components on Windows 10, version 1507 (Windows 10 Enterprise 2015 LTSB and Windows 10 IoT Enterprise 2015 LTSB). This was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8, a maximum severity of critical and flagged by Microsoft as exploited in-the-wild.
This vulnerability stems from how the Servicing stack handled the applicability of Optional Components as a result of a triggered code defect. This began with a security update released on March 12, 2024 - KB5035858 (OS Build 10240.20526). The affected Optional Components were flagged as “not applicable” and reverted to their Release To Manufacturing (RTM) version. Microsoft notes that only optional components enabled from the following list are affected:
- .NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services \ ASP.NET 4.6
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services
- Administrative Tools
- Internet Explorer 11
- Internet Information Services\World Wide Web Services
- LPD Print Service
- Microsoft Message Queue (MSMQ) Server Core
- MSMQ HTTP Support
- MultiPoint Connector
- SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support
- Windows Fax and Scan
- Windows Media Player
- Work Folders Client
- XPS Viewer
Successful exploitation would result in the rollback of previously mitigated vulnerabilities in the affected optional components in Windows 10 versions as specified above.
While this CVE has been labeled as exploited in-the-wild, confusingly Microsoft states that there is no evidence of direct exploitation of CVE-2024-43491,rather through observed rollbacks of CVEs related to Optional Components for Windows 10 (version 1507). Because some of these rolled back CVEs have been observed to have been exploited, this prompted Microsoft to apply the exploitability index assessment for this vulnerability as “Exploitation Detected.”
CVE-2024-38217 | Windows Mark of the Web Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38217 is a security feature bypass vulnerability affecting Mark of the Web, an identifier used by Windows to mark files that have been downloaded from the internet. With a CVSSv3 score of 5.4, Microsoft notes that it was exploited in the wild and publicly disclosed prior to the patch becoming available. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an attacker to convince a user into opening a specially crafted file that could evade Mark of the Web (MOTW) defenses.
Joe Desimone of Elastic Security published a blog post about the flaw in August, which includes an example of successful exploitation. The blog also highlights that Elastic Security "identified multiple samples in VirusTotal that exhibit the bug" with the oldest being submitted "over 6 years ago," indicating potential exploitation as far back as 2018.
An additional Mark of the Web security feature bypass vulnerability, CVE-2024-43487, was also patched this month. With a severity rating of moderate and a CVSSv3 score of 6.5, this flaw was rated as “Exploitation Less Likely” according to the Microsoft Exploitability Index. As with CVE-2024-38217, successful exploitation would involve the attacker convincing a user to open a specially crafted file.
This is the second month in a row that a MOTW security feature bypass vulnerability was exploited in the wild as a zero-day, as Microsoft published an CVE-2024-38213 in August, though this flaw was originally patched as part of its June 2024 Patch Tuesday.
CVE-2024-38014 | Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38014 is an EoP vulnerability affecting Windows Installer which was observed as being exploited as a zero-day. While Microsoft did not share any details on exploitation, the advisory does note that successful exploitation would grant the attacker SYSTEM level privileges. As with other EoP vulnerabilities, these vulnerabilities are often used as part of post-compromise activity in order to further compromise a network using elevated account privileges.
CVE-2024-38226 | Microsoft Publisher Security Features Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38226 is a security feature bypass vulnerability affecting Microsoft Publisher. This vulnerability was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 7.3 and has been exploited in the wild as a zero-day. In order to exploit this flaw, an attacker must be authenticated to a target system and convince a user to download a crafted file. This would allow a local attacker to bypass Office macro policies designed to block untrusted and potentially malicious files on the target’s system. According to the advisory, the Preview Pane is not an attack vector for this vulnerability.
CVE-2024-26186, CVE-2024-26191, CVE-2024-37335, CVE-2024-37338, CVE-2024-37339 and CVE-2024-37340 | Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-26186, CVE-2024-26191, CVE-2024-37335, CVE-2024-37338, CVE-2024-37339 and CVE-2024-37340 are a series of RCE vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring. All six of these vulnerabilities are rated as important, were assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.8, an exploitability index assessment of “Exploitation Less Likely” and were attributed to Andrew Ruddick with Microsoft Security Response Center.
Microsoft's FAQ for these vulnerabilities state “successful exploitation of this vulnerability requires an authenticated attacker to leverage SQL Server Native Scoring to apply pre-trained models to their data without moving it out of the database.” While the SQL Server vulnerabilities primarily enable unauthorized data manipulation, they could hypothetically lead to RCE if combined with additional security flaws or misconfigurations that allow SQL command execution.
CVE-2024-37337, CVE-2024-37342 and CVE-2024-37966 | Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring Information Disclosure Vulnerability
CVE-2024-37337, CVE-2024-37342 and CVE-2024-37966 are information disclosure vulnerabilities affecting Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring. All three of these vulnerabilities are rated as important, and were assigned a CVSSv3 score of 7.1 and exploitability index assessment of “Exploitation Less Likely.” These CVEs are also attributed to Andrew Ruddick with Microsoft Security Response Center, bringing the Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring CVE count to seven in September’s Patch Tuesday release, accounting for over 10% of the CVEs this month. Successful exploitation of this vulnerability by a threat actor with authenticated access to Microsoft SQL Server Native Scoring could potentially allow the reading of small portions of heap memory. The disclosed memory could contain sensitive data, including user credentials, session tokens, or application-level information, which may lead to further security risks.
CVE-2024-38018 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2024-38018 is a critical severity RCE affecting Microsoft SharePoint Server with a CVSSv3 score of 8.8 and an exploitability index assessment of “Exploitation More Likely.” While Microsoft has provided no information on exploitability, a threat actor would generally need to be authenticated and have sufficient permissions for page creation to take advantage of this RCE in Microsoft SharePoint Server.
Tenable Solutions
A list of all the plugins released for Microsoft’s September 2024 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
For more specific guidance on best practices for vulnerability assessments, please refer to our blog post on How to Perform Efficient Vulnerability Assessments with Tenable.
Get more information
- Microsoft's September 2024 Security Updates
- Tenable plugins for Microsoft September 2024 Patch Tuesday Security Updates
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management
- Exposure Management

